Have you ever wondered why you automatically reach for the same coffee brand every morning? Or why you check your favorite shopping app without even thinking about it? There’s fascinating brain science behind these automatic behaviors – and smart businesses are using this knowledge to turn one-time buyers into loyal repeat customers.
Your brain is constantly rewiring itself based on your daily actions. This remarkable ability, called neuroplasticity, is the secret weapon that savvy marketers are now using to create unbreakable customer habits. By understanding how habits form in the brain, businesses can design experiences that keep customers coming back again and again.
In this article, you’ll discover:
- How your brain physically changes when forming habits
- The simple three-part loop that creates customer loyalty
- Practical strategies to build habit-forming business experiences
- How leading companies are using these brain-based techniques
- Ethical considerations to keep in mind
Ready to unlock the secrets of the habit-forming brain and transform casual browsers into loyal customers? Let’s dive in!
The Neuroscience of Habit Formation
Your brain is remarkably adaptable. Every time you repeat an action, physical changes occur that make that behavior easier and more automatic the next time. This is the foundation of habit formation, and it has everything to do with how our brains are wired.
Neuroplasticity Fundamentals
At its core, neuroplasticity is your brain’s ability to reorganize itself by forming new neural connections. Think of your brain as a forest with countless pathways. When you repeatedly take the same path, it becomes wider and easier to travel – that’s essentially what happens in your brain when habits form.
When customers repeatedly engage with your business, their brains are physically changing in ways that make returning to you the path of least resistance. This happens through two main types of plasticity:
- Synaptic plasticity: When customers repeat an action (like checking your app or visiting your store), the connections between their neurons strengthen, making the behavior more automatic.
- Structural plasticity: With continued repetition, actual physical changes occur in the brain, creating dedicated neural pathways for the habitual behavior.
The brain region called the basal ganglia plays a crucial role here. As behaviors become more automatic, control shifts from the thinking part of the brain to this region, which specializes in routine actions. This is why loyal customers can make purchases from your business almost without thinking!
The Habit Loop (Cue-Routine-Reward Cycle)
Every habit your customers form follows a predictable pattern called the Habit Loop, first popularized by Charles Duhigg in his book “The Power of Habit.” Understanding this three-part cycle gives you a framework for creating customer loyalty:
- Cue: The trigger that initiates the behavior. For businesses, this could be mobile notifications, email reminders, distinctive packaging, or even certain times of day.
- Routine: The behavior itself. This might be opening your app, browsing your store, or completing a purchase.
- Reward: The pleasure or benefit that reinforces the habit. Each time a customer receives a reward (like a discount, a pleasant shopping experience, or social recognition), their brain releases dopamine, strengthening the entire habit loop.
By thoughtfully designing each element of this loop, you can create powerful customer habits that drive repeat business.
Neural Mechanisms Driving Repetition
The brain’s reward system plays a starring role in habit formation. When customers engage with your business and receive something they value, their brains release dopamine – a neurotransmitter associated with pleasure and reward.
What’s particularly interesting is how this system evolves. Initially, dopamine is released when the customer receives the reward. But over time, the brain begins to release dopamine in anticipation of the reward. This shift is called “reward prediction error” and it’s what makes habits so powerful – your customers’ brains begin to crave the experience your business provides even before they engage with you.
During early habit formation, the prefrontal cortex (the thinking, decision-making part of the brain) is highly active. But as the habit strengthens, the basal ganglia takes over, making the behavior more automatic and requiring less conscious thought. This transition is why strong customer habits can persist even when competitors offer seemingly better deals.
Now that we understand how the brain creates habits, let’s explore how businesses can strategically apply this knowledge to build customer loyalty. After all, knowing how habits form is one thing – but designing experiences that leverage this knowledge is where the real magic happens!
Strategic Framework for Habit-Driven Customer Retention
Armed with knowledge of how the brain forms habits, it’s time to put this science to work. By strategically designing each element of the habit loop, you can create customer experiences that naturally lead to repeat business. Let’s break down how to optimize each component.
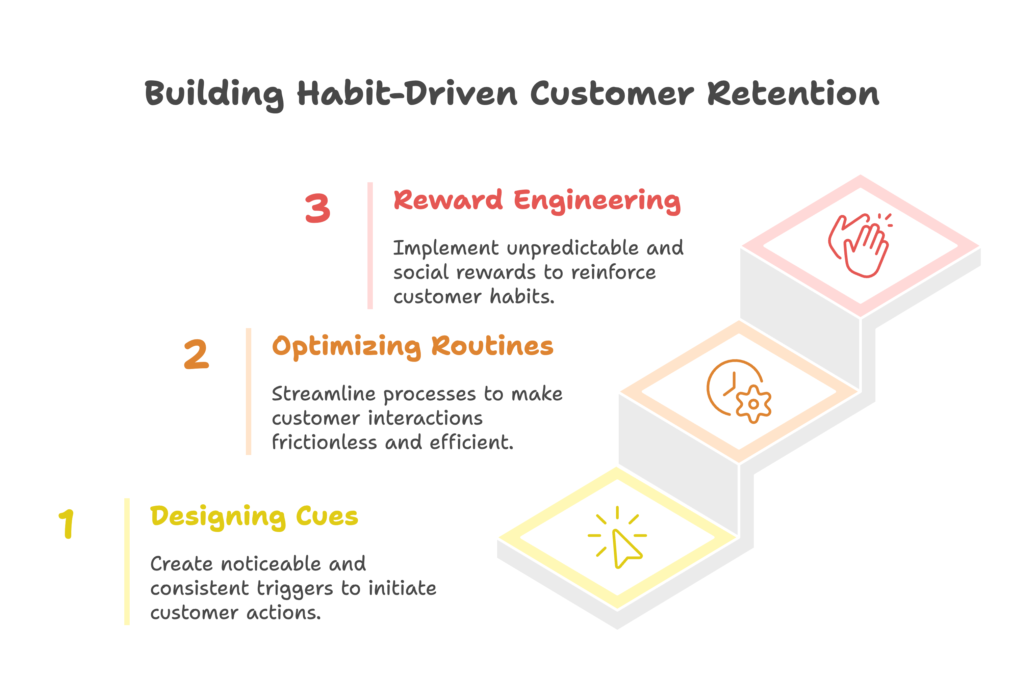
Designing Effective Cues
Cues are the triggers that initiate habitual behavior. The more noticeable and consistent your cues, the more effective they’ll be at triggering your desired customer actions. Here’s how to create powerful cues:
- Multi-sensory triggers: Engage multiple senses for stronger associations. Think of Starbucks’ distinctive coffee aroma, McDonald’s visual golden arches, or Netflix’s familiar “ta-dum” sound. Which of your brand elements could become recognizable sensory cues?
- Context-aware notifications: Send mobile alerts at times when customers are most receptive. A food delivery app might send lunchtime notifications, while a fitness brand might cue workouts in the morning.
- Branded micro-moments: Insert your brand into daily routines. For example, a skincare brand might create morning and evening ritual cues, while a news app could become part of the wake-up routine.
The key is consistency. Each time your cue appears in the same context, it strengthens the neural pathway leading to the routine behavior you want to encourage.
Optimizing Routines for Neural Efficiency
Once a cue has triggered interest, the customer enters the routine phase. This is the actual behavior you want to become habitual. The brain loves efficiency, so making this phase as frictionless as possible is crucial:
- Frictionless processes: Remove obstacles to completion. Aim for checkout processes that require three clicks or fewer. Each additional step reduces the chance of habit formation.
- Predictive UX patterns: Use customer history to anticipate needs. Amazon’s “Buy Again” feature reduces friction by making repeat purchases nearly effortless.
- Gamified interactions: Add enjoyable elements to routine behaviors. Progress bars, streak counts, and achievement systems tap into the brain’s love of completion and mastery.
Remember that the prefrontal cortex – the decision-making part of the brain – is active during early habit formation. By making routines simple and predictable, you help the behavior shift to the automatic control of the basal ganglia more quickly.
Reward Engineering for Dopamine Optimization
Rewards are the payoffs that reinforce the entire habit loop. They trigger dopamine release in the brain, cementing the neural pathways that lead customers back to your business. Here’s how to create effective rewards:
- Variable ratio reinforcement: Unpredictable rewards create stronger habits than predictable ones. Consider how social media platforms sometimes give lots of engagement and sometimes little – this uncertainty keeps users coming back to check. You could implement “surprise” discounts or occasional free gifts rather than entirely predictable rewards.
- Social validation rewards: Humans are wired to value social approval. Features that showcase customer content, reviews, or achievements leverage this desire for social connection and recognition.
- Surprise-and-delight mechanics: Unexpected positive experiences create powerful dopamine hits. Consider how you might occasionally exceed customer expectations in ways they weren’t anticipating.
The most effective rewards align with customer motivations while being just valuable enough to reinforce the habit without breaking your budget.
With our framework for creating habit-forming experiences in place, you might be wondering: how do we measure whether these efforts are actually working? Let’s explore the metrics that can help you track neuroplastic habit formation in your customer base.
Metrics for Neuroplastic Habit Formation
Creating habit-forming experiences is one thing, but how do you know if they’re working? While we can’t directly see neural pathways forming in customers’ brains, we can measure behaviors that indicate habit formation.
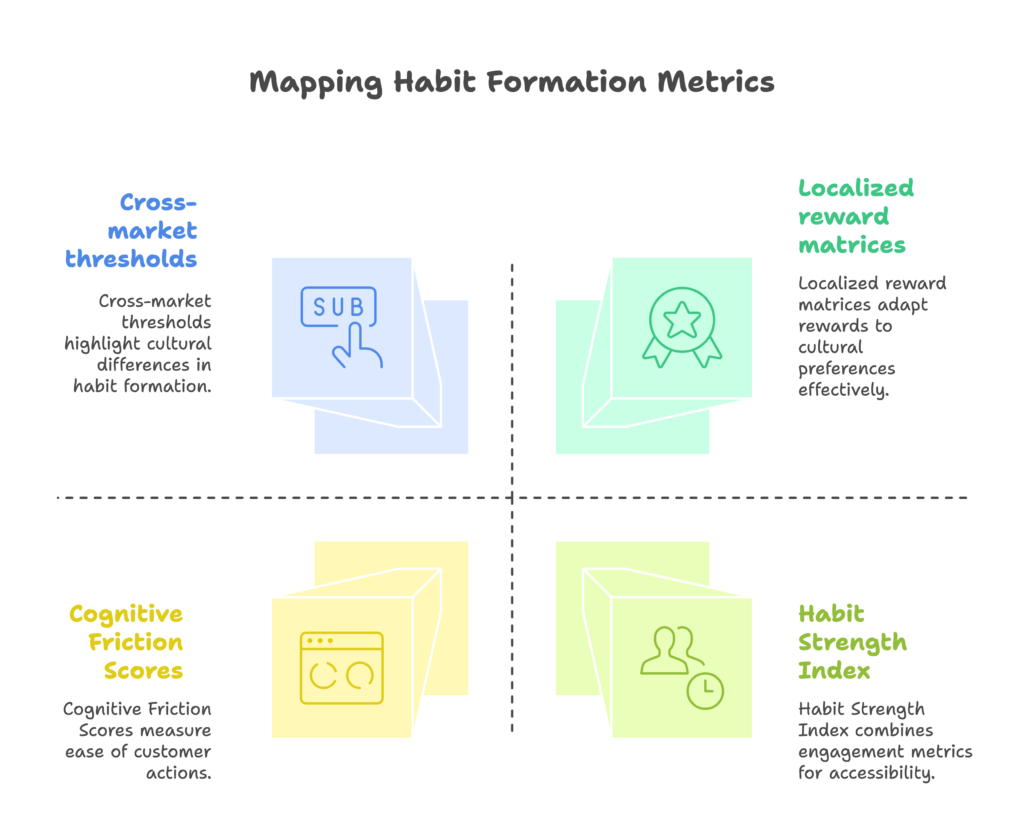
Let’s explore both traditional and innovative approaches to tracking customer habits.
Behavioral Metrics
These practical measurements help you assess habit strength without needing brain scans:
- Habit Strength Index (HSI): Combine frequency (how often customers engage), consistency (regularity of engagement), and emotional engagement (sentiment measures) to create a single metric of habit strength.
- Neural Retention Rate (NRR): Track repeat purchase behavior at 30, 60, and 90-day intervals. Strong habits show consistent or increasing engagement over these timeframes.
- Cognitive Friction Scores: Measure how quickly and easily customers complete desired actions. Decreasing time-to-completion often indicates strengthening habits.
For example, a coffee shop app might track how consistently customers order their morning coffee (consistency), how frequently they use the app overall (frequency), and sentiment measures from in-app feedback (emotional engagement) to calculate their HSI.
Advanced Neurometric Tracking
For companies with research budgets, more direct neurological measurements are becoming available:
- EEG measurements: Electroencephalography can measure prefrontal cortex engagement, helping identify when customers are in early vs. late stages of habit formation.
- fMRI analysis: Functional magnetic resonance imaging can show basal ganglia activation patterns, indicating automated behavior.
- Pupillometry: Measuring pupil dilation provides real-time data on reward response and emotional engagement.
While these advanced methods might seem futuristic for most businesses, partnering with research institutions or neuromarketing firms can make them accessible for important product testing.
Cultural Adaptation
Habit formation isn’t universal – it varies across cultures, regions, and demographics. Smart companies track these differences:
- Cross-market thresholds: The number of repetitions needed for habit formation varies by culture. Some markets may require more consistent experiences before habits form.
- Localized reward matrices: Different cultures value different types of rewards. What’s motivating in one market may fall flat in another.
- Generational profiles: Age groups respond differently to habit formation techniques. Younger consumers may form digital habits more quickly, while older consumers might value different reward types.
By segmenting your metrics across these dimensions, you can fine-tune your habit formation strategies for different customer groups.
Now that we have a framework for designing habit-forming experiences and metrics for measuring success, let’s get practical. How exactly do you implement these insights in your business? Let’s explore some actionable implementation strategies next.
Implementation Strategies
Understanding the science is fascinating, but applying it is where real business results happen. Let’s explore practical implementation strategies that turn neuroplasticity concepts into customer retention tools.
Personalized Habit Pathways
No two customers are exactly alike. Their brains form habits differently based on personal preferences, past experiences, and individual motivations. Here’s how to personalize the habit loop:
- AI-driven cue customization: Use customer data to deliver personalized triggers. A fitness app might send workout reminders at the specific time each user historically engages most.
- Dynamic routine adaptation: Adjust processes based on customer behavior patterns. An e-commerce site might simplify the purchasing flow for returning customers or modify category displays based on browsing history.
- Reward personalization: Offer incentives tailored to individual preferences. Some customers might value exclusive content while others prefer discounts or recognition.
Personalization makes each element of the habit loop more effective by aligning with existing neural patterns in your customers’ brains.
Gamification Architectures
Games are masters of habit formation. By incorporating game-like elements into your customer experience, you can tap into powerful motivational systems:
- Progress bar psychology: Visual progress indicators create a sense of investment and tap into the completion bias – our desire to finish what we’ve started. Loyalty programs with visible progress toward rewards leverage this psychology.
- Badge-earning reinforcement: Achievement recognition systems provide social validation and status indicators. Digital badges or status levels give customers bragging rights and visible signs of loyalty.
- Loss aversion mechanics: The fear of losing something is more motivating than gaining something equivalent. Limited-time offers, expiring points, or membership benefits that could be lost create powerful motivation to maintain habits.
These game-inspired elements make the routine phase more engaging while enhancing the reward experience.
Ethical Habit Formation Guidelines
With great power comes great responsibility. As you implement neuroplasticity-based strategies, ethical considerations should guide your approach:
- Transparency in reward schedules: Be clear about how and when customers earn rewards. Hidden or deceptive systems might work short-term but damage trust long-term.
- Cognitive overload prevention: Avoid overwhelming customers with too many cues or complex routines. Mental fatigue works against habit formation and customer satisfaction.
- Addiction risk monitoring: Regular assessment of customer behavior patterns can identify potentially unhealthy usage. Implement safeguards like usage limits or break reminders for products with addictive potential.
Ethical habit formation creates sustainable business relationships that benefit both your company and your customers.
While these strategies sound promising, you might be wondering if they really work in the real world. Let’s look at some powerful examples of companies successfully applying these principles to create loyal customer habits.
Case Studies in Neural Habit Formation
Theory is valuable, but seeing these principles in action brings them to life. Here are three companies that have masterfully applied neuroplasticity concepts to create strong customer habits.
Starbucks’ Mobile Ordering Ecosystem
Starbucks has created one of the most successful habit-forming mobile experiences in retail. Here’s how they’ve applied neuroplasticity principles:
- Cue: Geolocation triggers send notifications when customers are near a store, and morning routines become associated with the Starbucks app.
- Routine: One-tap ordering removes friction from the purchase process. Saved favorites and predictive suggestions make reordering nearly effortless.
- Reward: Immediate rewards via points balance updates and progress animations create dopamine hits with each purchase.
The results speak for themselves: 42% of U.S. Starbucks sales now come through their mobile ecosystem, with habitual app users visiting more frequently than non-app customers.
Amazon Prime’s Subscription Habit Loop
Amazon has built perhaps the strongest customer habit platform in e-commerce through its Prime membership program:
- Cue: The Prime shipping promise creates a trigger for customers to check Amazon first when they need something. The prominent Prime logo serves as a visual cue throughout the experience.
- Routine: One-click ordering and simplified reordering make purchasing almost thoughtless, activating the basal ganglia’s automatic processing.
- Reward: Immediate gratification through fast shipping combines with bundled rewards like video and music services, creating multiple dopamine pathways.
This carefully designed habit loop has resulted in an astonishing 93% renewal rate after Year 1 of Prime membership, with members spending more than double what non-Prime customers spend annually.
Duolingo’s Language Learning Habits
Duolingo has turned language learning – traditionally challenging to maintain – into a daily habit for millions:
- Cue: Streak counts and carefully timed notifications serve as powerful triggers. The fear of breaking a streak activates loss aversion, while cute characters create emotional connection.
- Routine: Bite-sized, 5-minute lessons lower the activation energy required to start a session. The predictable lesson format allows the brain to process the experience automatically.
- Reward: Immediate XP, level-ups, and engaging reward animations create consistent dopamine release that reinforces the habit.
Through these neuroplasticity-based design choices, Duolingo has achieved a 300% increase in 180-day retention compared to earlier versions of their app.
These case studies show the remarkable business results possible when applying brain science to customer experience design. But as we harness these powerful tools, important ethical questions arise. Let’s explore the responsibilities that come with shaping customer habits.
Ethical Considerations & Future Directions
With great power comes great responsibility. As businesses embrace neuroplasticity-based approaches to customer retention, ethical considerations become increasingly important. At the same time, emerging technologies are opening new possibilities in this field. Let’s explore both the ethical boundaries and future horizons of habit-based marketing.
Neuroethical Boundaries
As we gain more powerful tools to influence customer behavior, clear ethical guidelines become essential:
- Dark pattern prevention: Avoid manipulative cue designs that trick customers into unintended actions. Ethical habit formation should enhance customer lives, not exploit vulnerabilities.
- Dopamine exploitation guidelines: Be mindful of how reward systems might affect vulnerable individuals. Excessive variable rewards can lead to unhealthy usage patterns in some users.
- Vulnerable population protections: Extra care should be taken when designing for children, the elderly, or those with cognitive impairments who may be more susceptible to habit-forming techniques.
The most sustainable approach is to align habit formation with genuine customer benefit. When habitual engagement with your business genuinely improves customers’ lives, the ethical equation balances positively.
Emerging Technologies
The frontier of neuroplasticity-based marketing continues to advance with new technologies:
- VR/AR habit environments: Virtual and augmented reality create immersive spaces for forming powerful multi-sensory habits. Imagine virtual shopping experiences that create stronger neural pathways than screen-based interactions.
- Biometric wearables: Smartwatches and fitness trackers increasingly allow real-time adaptation based on physiological states. Future marketing could adjust cues and rewards based on actual neural states.
- Advanced prediction models: Machine learning is improving our ability to predict individual habit formation patterns. This could allow for precisely targeted interventions at the moment when a customer is most receptive to forming a new habit.
These emerging technologies offer exciting possibilities while raising important new ethical questions that the industry must address proactively.
Sustainable Habit Engineering
The most forward-thinking companies are exploring how habit formation can serve broader goals:
- Circular economy systems: Habits can be formed around sustainable practices like recycling packaging or participating in product take-back programs.
- Altruistic dopamine pathways: Social impact initiatives tied to purchases can create reward responses from knowing a purchase helps others. This creates positive associations beyond the product itself.
- Loyalty decay prevention: Sophisticated algorithms can detect early warning signs of habit weakening and trigger re-engagement before a customer churns completely.
These approaches point toward a future where neuroplasticity-based marketing creates value for businesses, customers, and society simultaneously.
Conclusion
The science of neuroplasticity offers powerful insights into creating lasting customer relationships. By understanding how the brain forms habits through the cue-routine-reward loop, businesses can design experiences that naturally lead to repeat engagement.
The most effective implementations personalize each element of the habit loop, measure results through both behavioral and advanced metrics, and maintain strong ethical boundaries. As seen in our case studies, companies that successfully apply these principles can achieve remarkable customer retention and growth.
As you apply these insights to your own business, remember that the goal isn’t manipulation, but rather creating genuinely valuable experiences that customers want to repeat. When your business becomes a positive habit in your customers’ lives, everyone wins.
Looking to put these neuroplasticity principles into practice? Shopify store owners can leverage the Growth Suite app to implement many of these habit-forming strategies automatically. From personalized triggers to optimized checkout flows and custom reward systems, Growth Suite helps you build the neural pathways that turn browsers into loyal, habitual customers.
References
- Arkam, H. (2024). The Neuroscience of Habit Formation. LinkedIn.
- Harvard DCE (2024). Neuromarketing Basics.
- Novus Loyalty (2024). Neuroscience & Retention.
- FasterCapital (2024). Neuroplasticity in Habit Formation.
- Neurolab360 (2021). Repetition Principles.
- Neuron Marketing (2024). Habit Triggers.