Have you ever filled your online cart with items you really wanted, only to feel a small pang of guilt as you hover over the “Proceed to Checkout” button? Or maybe you’ve bought something and felt uneasy afterward? This article is for you! By reading on, you will discover how guilt prevents customers from buying with confidence and explore ways to make shopping feel truly guilt-free. Ready to reduce those emotional barriers and increase conversions? Let’s dive in!
In this section: We’ll define how guilt appears in consumer contexts, learn how it affects sales, and understand why solving this issue can give businesses a real competitive edge.
Defining Consumer Guilt and Its Impact
Consumer guilt happens when shoppers feel uneasy or conflicted about their spending choices—whether due to ethics, finances, or personal values. Studies show that about 68% of potential buyers back out of purchases because of guilt or ethical concerns. This isn’t just an emotional issue; it has significant economic consequences. Brands miss out on sales, and shoppers might develop negative feelings toward companies they once trusted. Over time, guilt becomes a major emotional barrier to hitting that “Buy Now” button.
The Emergence of Guilt-Free Consumption as a Market Trend
Over the years, consumer mindsets have shifted from traditional, “buy without question” attitudes to guilt-free consumption (GFC). The popular trends platform TrendWatching identified *guilt-free consumption* back in 2013, and since then, ethical and mindful purchasing has grown even more important. Shoppers are now looking for goods and services that fit into their personal ethics and lifestyles—meaning they want to buy without regret or moral conflict.
The Business Case for Addressing Consumer Guilt
When companies tackle consumer guilt, they often see better conversion rates and higher customer satisfaction. Why? Because if people feel emotionally comfortable with a brand’s products or ethics, they’ll be less hesitant to purchase and more likely to come back. This positivity also benefits overall brand equity: by showing empathy and addressing guilt triggers, a business can build lasting relationships that competitors find hard to break.
You’ve learned how guilt shapes sales outcomes. Next, we’ll explore the deeper psychology behind why guilt arises in the first place.
The Psychology of Consumer Guilt
In this section: We’ll uncover the mental processes that lead to guilt, identify the various forms of guilt shoppers feel, and look at how this emotion can emerge before, during, or after a purchase.
Cognitive Mechanisms Behind Consumer Guilt
One key psychological driver is cognitive dissonance: we hold personal beliefs, but our actions may conflict with them. If someone values sustainability but buys from a brand with questionable practices, guilt can kick in. Similarly, people may want to maintain a positive self-image—so if an impulse buy contradicts their budget or values, they feel unsettled. These internal “value vs. action” clashes trigger emotional discomfort, which can quickly derail a purchase.
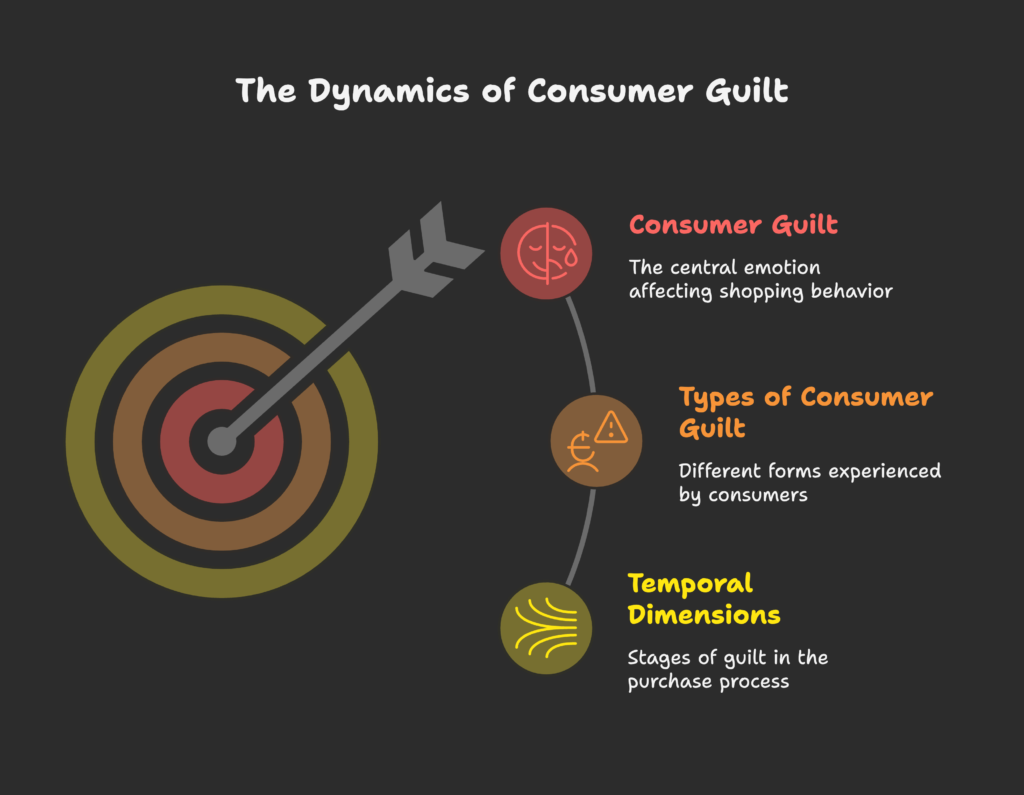
Types of Consumer Guilt
- Financial Guilt: Concerns about spending too much money or breaking a budget.
- Ethical Guilt: Worries about environmental harm, labor exploitation, or animal welfare.
- Health Guilt: Regret about buying junk food or ignoring fitness priorities.
- Social Responsibility Guilt: Feeling you’re not doing enough for your community or family.
- Moral Guilt: Violations of personal or religious standards.
Temporal Dimensions of Guilt in the Purchase Process
- Anticipatory Guilt: Anxiety before buying, often causing hesitation or cart abandonment.
- Proceeding Guilt: The discomfort at the moment of payment—leading to last-minute order cancellations.
- Reactive Guilt: Post-purchase remorse, sometimes prompting returns or refund requests.
Each type of guilt can impact a different step in the conversion funnel, so addressing them effectively requires a holistic view.
Now we know how guilt forms. Next, let’s see how it actually shows up in real-world shopping behaviors.
How Consumer Guilt Manifests in Purchasing Behavior
In this section: We’ll break down specific shopper behaviors that point to guilt, look at which product categories are most vulnerable, and see how different consumer groups handle guilt.
Behavioral Indicators of Guilt-Driven Decision-Making
- Cart Abandonment: Customers fill up their carts but leave the site or app without checking out when guilt strikes.
- Prolonged Browsing: People keep comparing items or reading reviews to avoid making a “wrong” or “guilt-ridden” choice.
- Delay Tactics: Users might bookmark or “save for later,” hoping to resolve their internal conflict or find moral justification.
- Post-Purchase Rationalization: Justifying a purchase to themselves or friends, often revealing underlying guilt.
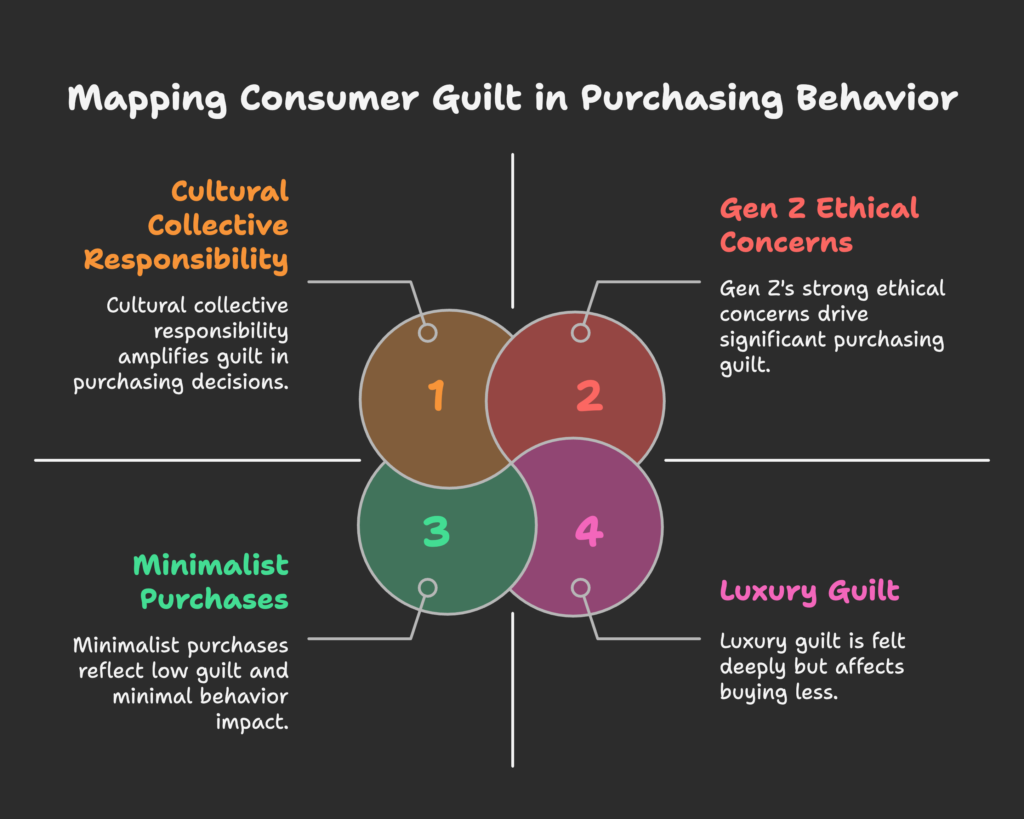
Product Categories Most Affected by Consumer Guilt
High-end luxury goods often trigger guilt due to their price tag. Similarly, items seen as indulgent or harmful to the environment—such as single-use plastics or fast fashion—can set off ethical guilt. Another example is “junk food,” where health concerns spark regret. Essentially, any product with potential moral, financial, or social implications could amplify guilt.
Consumer Segments and Guilt Sensitivity
Not everyone reacts the same way. Younger consumers, especially Gen Z, often demonstrate strong ethical standpoints, quickly feeling guilt if brand practices seem questionable. Meanwhile, certain cultural settings place a higher emphasis on collective well-being, intensifying social responsibility guilt. Marketers who understand these nuances can tailor guilt-reducing strategies more effectively.
We’ve identified the signs. Next, we’ll explore how to build frameworks that address guilt throughout the entire purchase experience!
Strategic Frameworks for Creating Guilt-Free Purchasing Experiences
In this section: We’ll outline methods to combat guilt at the source—through transparency, reframing value, highlighting ethical credentials, and offering justification frameworks that resonate with consumers’ needs.
Transparency and Information Strategies
- Supply Chain Visibility: Show consumers exactly where materials come from and how workers are treated. This alleviates ethical guilt.
- Clear Pricing Rationale: Being open about costs, fair wages, or sustainability expenditures fosters trust and quells suspicion.
- Educational Content: Proactive resources answer typical guilt triggers—like product origin or environmental impact—reducing worry.
Value Reframing Approaches
- Investment Mindset: Instead of highlighting price, stress quality, durability, or the personal benefits of a purchase.
- Longevity Over Disposability: Emphasize how your product lasts longer or reduces waste, so the cost feels more justifiable.
- Emotional Benefits: Show how your product alleviates stress, provides joy, or supports a meaningful cause.
Ethical Positioning Strategies
Brands can align with recognized certifications (like Fair Trade or cruelty-free seals) and publicize them. This quickly communicates credibility and reduces doubt. Showcasing real-world stories—like local community impact or a smaller carbon footprint—lets customers see exactly how their purchase makes a positive difference.
Purchase Justification Frameworks
Sometimes a shopper just needs a rationale like “I’ve worked hard; I deserve this” or “This is self-care, not indulgence.” Marketers can gently reinforce these perspectives, positioning the product as a well-earned treat, or a healthier, more ethical alternative. That context can remove guilt from the equation and seal the deal.
You’ve seen the big-picture strategies. Let’s discover how to apply them at each stage of the buying journey, from before they even add items to the cart to well after checkout!
Tactical Implementation Across the Consumer Journey
In this section: We’ll map out specific tactics at the pre-purchase stage, at the point of purchase, and after the deal is done—ensuring guilt never has a chance to creep in.
Pre-Purchase Guilt Mitigation
- Educational Landing Pages: Provide data on product ethics, cost breakdowns, or how the purchase supports good causes.
- Social Proof: Testimonials from happy, guilt-free customers reinforce that it’s a safe and positive decision.
- Value Comparison Tools: Let shoppers see the long-term savings or positive impact, countering financial or ethical hesitation.
- Anticipatory Guilt Reduction: Use friendly pop-ups that address common concerns and show how buying won’t conflict with personal values.
Point-of-Purchase Conversion Tactics
- Smooth Checkout: Make payment easy and highlight reassuring text about refunds, fair returns, or carbon offsets.
- Micro-Donations and Options: Offer a quick add-on donation to a cause or an eco-friendly upgrade—reducing any negative feelings.
- Instant Impact Visualization: Show real-time stats (“You’ve saved X amount of plastic” or “Your donation funds 1 tree”).
Post-Purchase Reassurance Strategies
- Thank-You Emails: Include a personalized message explaining the positive effects of the purchase.
- Community Involvement: Invite buyers to join a supportive group or forum that aligns with the brand’s mission.
- Long-Term Value Updates: Occasionally remind them of the ongoing benefits—like user tips, product care, or updates on charitable impacts.
Now let’s shift gears to the digital realm. Good user experience design is crucial for guiding shoppers through guilt-free decisions!
Digital and UX Design Elements for Guilt-Free Experiences
In this section: We’ll explore how to structure your website, content, and checkout to support guilt-free decision-making, from the first product page click to the final confirmation screen.
Website and App Design Considerations
- Ethical Badges and Cues: Prominently display eco-labels or certifications to build trust immediately.
- Clean, Trustworthy Layout: Avoid clutter; keep the design straightforward with strong calls to action that reassure rather than push.
- Progress Indicators: Show how far they’ve come in the checkout, each step reinforcing their positive choice.
Content Strategy for Guilt Mitigation
Craft narratives that resonate with moral or eco-conscious shoppers. Mix facts and figures (like carbon savings) with stories of real people or communities benefiting. Include testimonials that highlight how customers overcame guilt or found satisfaction. Provide balanced info—no manipulative hype—to empower, not pressure.
Cart and Checkout Optimization
- Abandonment Triggers: Detect when someone is hesitating and send a supportive reminder or clarify a common concern.
- One-Page Checkout: Fewer steps reduce mental strain, letting them finalize the order before guilt grows.
- Value Reinforcement: Summaries that restate the product’s top benefits or ethical pluses right before final payment.
Want real examples? Let’s explore how different industries are putting guilt-free tactics to work—and the outcomes they’re seeing.
Industry-Specific Applications and Case Studies
In this section: We’ll see how retailers, food brands, luxury goods, and financial services tackle guilt differently, offering insights and real-life stories of success.
Retail and E-commerce
Many retailers emphasize sustainable packaging or highlight worker welfare. Product pages might detail the source of materials or the brand’s commitment to fair wages. Some measure success through reduced returns and improved reviews. RetailMinded (2024) discusses how acknowledging environmental concerns fosters loyalty, boosting both conversions and brand love.
Food and Beverage
Health or diet guilt is common here. Emphasizing natural ingredients, transparent nutritional data, or ethical sourcing helps. A 2024 sugar-free tea packaging study found that honest labeling increased both trust and repeat purchases. Showing how the tea benefits health or the planet can be a potent guilt buster.
Luxury and Premium Categories
High price tags often prompt financial guilt. Successful luxury brands highlight craftsmanship and longevity—“You’re investing in an heirloom piece”—instead of “You’re splurging on a whim.” Some also demonstrate social contributions, like partnerships with artisans, to minimize moral conflict over spending on luxuries.
Financial Services
Spending on insurance, loans, or investments can trigger guilt if people feel uncertain. Clarity on terms, potential returns, and social responsibility can reduce reservations. Painting a picture of long-term financial health frames the service as self-care, turning guilt into a sense of security.
So far, we’ve learned the “how.” Next, let’s make sure we can measure our efforts, continually refining them to maintain a guilt-free edge.
Measurement and Optimization of Guilt-Free Strategies
In this section: We’ll identify key metrics, testing methods, and improvement cycles that let you track how effectively you’re preventing guilt and winning customer trust.
Key Performance Indicators
- Conversion Rates: Watch for lifts after implementing guilt-reducing content or design changes.
- Cart Abandonment Rates: Falling abandonment indicates fewer guilt-based hesitations.
- Average Order Value (AOV): If customers feel good, they may add more items or choose premium options.
- Repeat Purchase and Loyalty: Guilt-free experiences often lead to higher retention and positive reviews.
Testing Methodologies
Simple A/B tests can compare checkouts with different trust signals or micro-donation options to see which approach best reduces guilt. User labs or focus groups can also highlight which messages resonate emotionally. Long-term, analyzing user feedback helps fine-tune these approaches—ensuring you don’t slip into manipulative territory.
Continuous Improvement Frameworks
- Data-Driven Optimization: Use analytics to spot friction points and rework your approach.
- Customer Feedback Loops: Surveys, reviews, and direct interactions help detect evolving guilt triggers.
- Benchmarking: Keep an eye on what competitors do, especially if they solve guilt issues more effectively.
We’ve covered how to measure success. Next, let’s discuss ethical boundaries so we don’t cross the line from helping customers to manipulating them.
Ethical Considerations and Potential Pitfalls
In this section: We’ll reflect on how guilt-free strategies can sometimes go wrong, from manipulative marketing to ignoring cultural nuances, and how to avoid such traps.
Balancing Persuasion and Manipulation
Pushing empathy and transparency can be a double-edged sword. If it’s genuine, customers appreciate it. If it’s faked or exaggerated, it’s manipulative. Once trust is lost, it’s tough to regain. The best approach is to maintain honest communication and ensure your “ethical” claims hold up under scrutiny.
Interpassivity and Responsibility Transfer
Some consumers rely on brands to do the moral thinking for them—buying “ethical” items to feel personally absolved. If a company exploits that desire without truly delivering on promises, it fosters shallow changes rather than real improvements. Striking a balance between encouraging better choices and overstating solutions is crucial for genuine brand integrity.
Inclusivity and Accessibility in Guilt-Free Strategies
Price points often rise for sustainable or organic options, risking exclusivity. Strive for more inclusive solutions—like lower-cost lines or discount programs—so all income levels can access guilt-free goods. Culturally, certain markets may stress environmental guilt, while others care more about local labor conditions, so tailor your approach accordingly.
So we’ve handled the ethical side. Let’s look ahead at the future, from new tech to evolving consumer habits!
Future Trends in Guilt-Free Purchasing
In this section: We’ll consider upcoming technologies, changing consumer expectations, and potential regulations that could shape guilt-free marketing over the next few years.
Technological Developments
- AI and Personalization: Real-time identification of consumer guilt triggers allows tailored messages or product suggestions.
- Blockchain Verification: Enhanced supply chain transparency, letting shoppers confirm ethical sourcing with a quick scan.
- AR Impact Previews: Augmented reality could show environmental or social impacts, instantly clarifying guilt concerns.
Evolving Consumer Expectations
Ethical standards keep rising, with younger shoppers pushing for greater accountability. They want more than superficial claims—they want proof. “Guilt-free” will evolve from a nice bonus to a baseline expectation. Cross-cultural shifts will also matter, as different regions emphasize different guilt triggers, from water usage to local labor issues.
Regulatory and Industry Standards
We may see more legal frameworks ensuring transparent product labeling, especially for sustainability or social responsibility. Industry self-regulations could tighten, with certifications becoming mandatory in certain niches. As “guilt-free” goes mainstream, enforcement of honest claims will likely intensify.
Excited about what’s next? Let’s close with key recommendations to effectively remove emotional barriers and turn guilt into a thing of the past.
Conclusion and Strategic Recommendations
In this section: We’ll wrap up the main points on addressing consumer guilt and provide an actionable roadmap for businesses eager to embrace guilt-free positioning. We’ll also see how it can set you apart in competitive markets.
Core Principles for Effective Implementation
- Authenticity: Don’t fake sustainability or ethics. Genuine efforts earn lasting trust.
- Balanced Information: Combine transparent facts with reassuring emotional support.
- Real Value: Show how your offering genuinely benefits the customer and the greater good.
- Long-Term Relationship Building: Address not only immediate guilt but also the evolving concerns of repeat customers.
Implementation Roadmap
- Guilt Triggers Assessment: Identify why your audience might feel guilty (pricing, ethics, etc.).
- Prioritize High-Impact Solutions: Tackle the biggest emotional barriers first—like supply chain transparency or loyalty program improvements.
- Phase the Changes: Start with simpler steps (clearer product info), then add bigger improvements (charity tie-ins, advanced tech).
- Measure & Adjust: Use analytics, feedback, and iteration to refine your guilt-free strategies over time.
Competitive Advantage Through Emotional Barrier Removal
When you systematically eliminate the guilt factor, your store or brand becomes an inviting space for conscious shoppers. This fosters higher conversion rates, deeper loyalty, and enthusiastic word-of-mouth referrals. Over time, you can position yourself as an industry leader that truly cares about its impact—and that resonates with modern consumers.
Quick Note: If you run a Shopify store and want to eliminate guilt from your customers’ journeys, consider the Growth Suite application. It helps you design smoother checkout experiences, highlight ethical practices, and keep your audience feeling great about every purchase—ultimately boosting sales and brand love.
References
- Aydin, H., & Ünal, S. (2015). Evaluation of the strategies coping with consumers’ guilt and shame in impulse buying: A study on university students. ISMA UFL Proceedings, 119-133. Link
- Blyth, M. (2016). Guilt-free food consumption: one of your five ideologies a day. Journal of Consumer Marketing, 33(7), 461-471. Link
- Burnett, M. S., & Lunsford, D. A. (1994). Conceptualizing guilt in the consumer decision-making process. Journal of Consumer Marketing, 11(3), 33-43. Link
- FasterCapital. (2024, June 15). Conversion Marketing: How to Use Psychology and Emotions to Boost Your Conversions. Link
- Mackenzie, S. (2013). Conditions for Guilt-Free Consumption in a Transnational Criminal Market. European Journal on Criminal Policy and Research, 20, 503-515. Link
- RetailMinded. (2024, January 6). How Retailers Can Offer A Guilt-Free Shopping Experience In 2024. Link
- CNBC. (2024, November 29). Applying this ‘$1 rule’ is the secret to guilt-free shopping, expert says. Link
- Neuroscience of Branding. (2025, February 7). Guilt, Dirty Money, and their Impact on Consumer Psychology. Link
- Semanticscholar. (2024, June 30). Study on the Impact of Packaging Design Elements and Perceived Value of Sugar-Free Tea Beverages on Consumer Purchasing Behavior. Link
- Spence, S. (2015). Anticipated Guilt and Ethical Consumption: The Moderating Role of Consumers’ Socially Responsible Consumption Behaviour. Brock University. Link
- TrendWatching. (2013, September 25). Guilt-free consumption. Link
- Wikipedia. (2023, July 20). Guilt-free consumption. Link