Have you ever wondered why certain products stand out in your memory while others fade away? Or why you often recall the first item you noticed on a page and the last product you scrolled past? If these questions spark your curiosity, you’re in the right place! By the time you finish reading this article, you’ll discover how a fascinating cognitive bias—known as the Serial Position Effect—can reshape your e-commerce strategies. Ready to explore how to make each product listing unforgettable? Let’s dive in!
Introduction to the Serial Position Effect
Welcome to the opening section, where you’ll learn the basic foundation of the Serial Position Effect and why it matters. By the end of this section, you’ll see how it underpins vital consumer decisions. Let’s start with some definitions, then we’ll move on to its components and commercial value. Once we wrap up here, you’ll be excited to discover the deeper cognitive science behind it all!
Definition and Psychological Foundation
The Serial Position Effect is a cognitive bias where people tend to remember the first and last items in a sequence more clearly than those in the middle. This concept dates back to pioneering work by Hermann Ebbinghaus in the late 1800s, further validated by researchers like Murdock and Bennet in the 1960s. The reason behind this effect is closely tied to how our memory processes information—our brains naturally struggle to encode and retrieve items that appear in the “forgotten middle.”
In consumer behavior, this effect is crucial. Shoppers often recall the first and last products they see, influencing what they buy or return to later. This limitation of memory can significantly impact purchase decisions, making it a powerful tool for online store owners and marketers seeking a competitive edge.
Before we dive into its components, keep in mind that the Serial Position Effect reveals just how much consumer choices hinge on memory. And if memory is at play, so is the opportunity for strategic placement. Next, we’ll explore the core aspects—primacy, recency, and the tricky middle.
Components of the Serial Position Effect
The Serial Position Effect is made up of two main forces: primacy and recency. As you learn about each, you’ll see how their interplay shapes how customers remember your products. We’ll also discuss what happens in that overlooked middle. After this, you’ll be ready to connect these elements directly to e-commerce strategy.
- Primacy Effect: We tend to recall items listed at the beginning because they have more time to be processed and stored in our long-term memory.
- Recency Effect: We remember items at the end because they linger in our short-term or working memory, especially if we’ve seen them most recently.
- The Forgotten Middle: The items in the middle often receive the least attention, making them easily overlooked. This is where potential bestsellers can vanish from consumer memory if not highlighted properly.
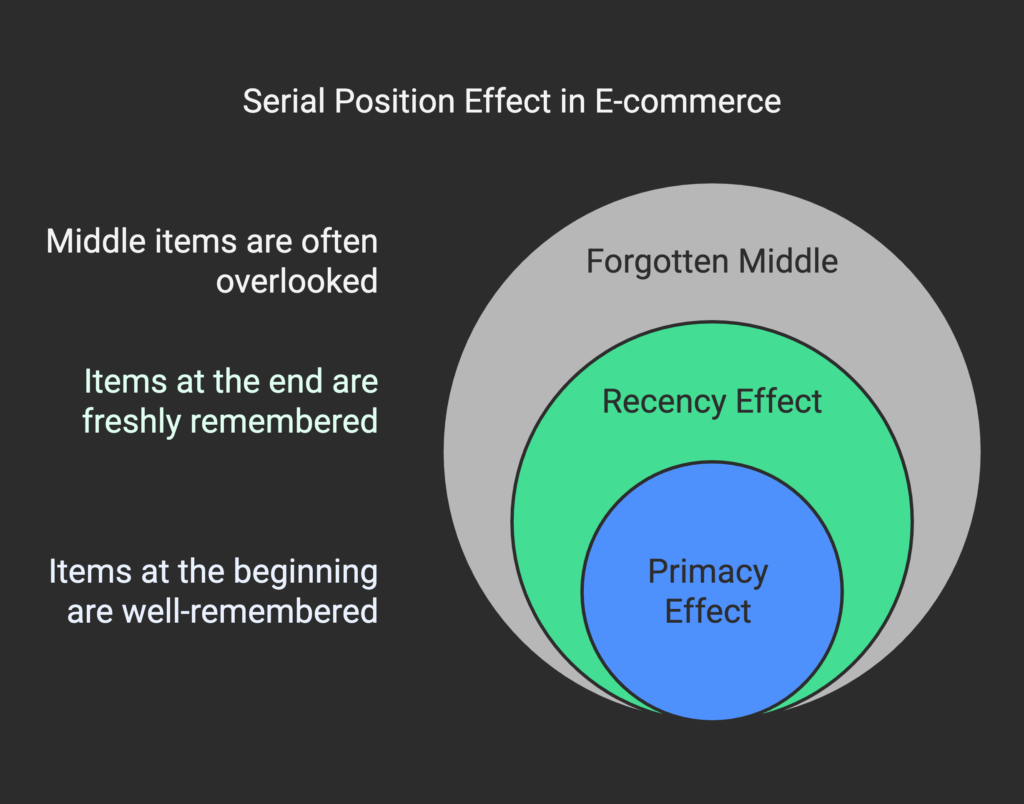
When plotted on a graph, the serial position curve typically shows higher recall for the first and last list items, with a dip in the middle. Understanding this curve is essential for creating product layouts that boost visibility and sales.
Now that you know the key components, we’ll soon connect them to real-world e-commerce practices. But first, let’s see exactly why this effect matters for online sellers like you.
Relevance to E-commerce and Product Listing Strategy
This is where things get practical. By the end of this subsection, you’ll grasp how listing positions can influence conversions. We’ll highlight success stories from major platforms and show you why tapping into consumer memory is a genuine competitive advantage.
- Statistical Evidence: Research shows that products placed at the beginning or end of a list can enjoy higher click-through and conversion rates.
- Perceived Importance: Consumers often assign more value to products at the top or bottom positions, assuming these placements indicate quality or special status.
- Existing Industry Usage: Big-name e-commerce platforms already leverage the Serial Position Effect by strategically placing sponsored items or bestsellers in prime spots.
- Competitive Edge: Understanding cognitive biases and memory limitations allows you to stand out in crowded markets. When you optimize placement, you meet shoppers’ expectations while subtly guiding their choices.
Now that we’ve laid the groundwork and shown how these ideas translate to e-commerce, get ready to explore the deeper mental processes behind the Serial Position Effect.
The Cognitive Science Behind the Serial Position Effect
In this section, we’ll unveil the science that powers the primacy and recency effects—from how the brain stores information to how consumers pay attention to product listings. By the end, you’ll see that memory and attention are tightly linked. Let’s begin with how our memory processes position information.
Memory Processing and Position Influence
Memory lies at the heart of the Serial Position Effect. When items appear at the start of a list, they get extra time to enter our long-term memory (primacy). Meanwhile, items at the end of a list persist in short-term memory (recency). Because of working memory constraints, we can only juggle so much information at once. That explains why the middle items often slip away. Also, the recency boost typically lasts about 30 seconds if not reinforced by repetition.
Thus, if you have a row of products, the first ones have an advantage in long-term storage, and the last ones benefit from being seen right before making a decision. Up next, let’s see how attention patterns reinforce these memory effects.
Attention Patterns and User Behavior
Did you know that eye-tracking studies often show people scan web pages in an “F-pattern” or “Z-pattern”? This means users devote more time to the top and bottom areas while skimming the middle. This visual bias is directly linked to memory formation—if shoppers don’t fixate on a product long enough, it’s less likely they’ll remember it later.
Heuristics also come into play. People are prone to mental shortcuts, especially online, where distractions abound. They quickly decide what’s important and what’s not, often focusing on items that either appear first or last in a listing. Interested in how personal factors also affect the Serial Position Effect? We’ll look into that now.
Psychological Factors Affecting Position Impact
Consumers are not all alike. Individual traits—like high motivation, purchase intent, or even demographic factors—can amplify or reduce the Serial Position Effect. Shoppers more emotionally invested in a category might pay closer attention throughout the list, while casual browsers may only remember the first and last items.
From age groups to personal shopping habits, these variables shape how strongly the primacy and recency effects show up. That’s why it’s important to recognize that while the Serial Position Effect is universal, its intensity can vary across your audience.
Understanding these aspects of cognitive science sets the stage for strategic implementation in your online store. Ready to apply this knowledge in concrete ways? Let’s continue!
Strategic Implementation in E-commerce Product Listings
Here, we’ll break down how to harness primacy and recency in practical ways—like optimizing your product page layout or deciding which products deserve top billing. By the end, you’ll have an arsenal of tactics to highlight your best offerings. Let’s start with overall layout.
Product Page Layout Optimization
A well-organized product page helps buyers find what they want and remember it. Whether you use a grid or list layout, being strategic about top and bottom positions can significantly improve results.
- Critical Product Placement: Ensure key products occupy first or last spots on category pages or featured lists.
- Grid vs. List: In a grid, the top-left and bottom-right items may gain special attention. In a list, the first and final positions are prime real estate.
- Sorting Options: If you allow customers to sort by price or popularity, consider how default sorting impacts which items appear at the top or bottom.
- Mobile Considerations: On smaller screens, vertical scrolling magnifies the Serial Position Effect, so watch those first and final positions with care.
Great layouts are just the beginning. Let’s see how you can specifically leverage the power of first-position products next.
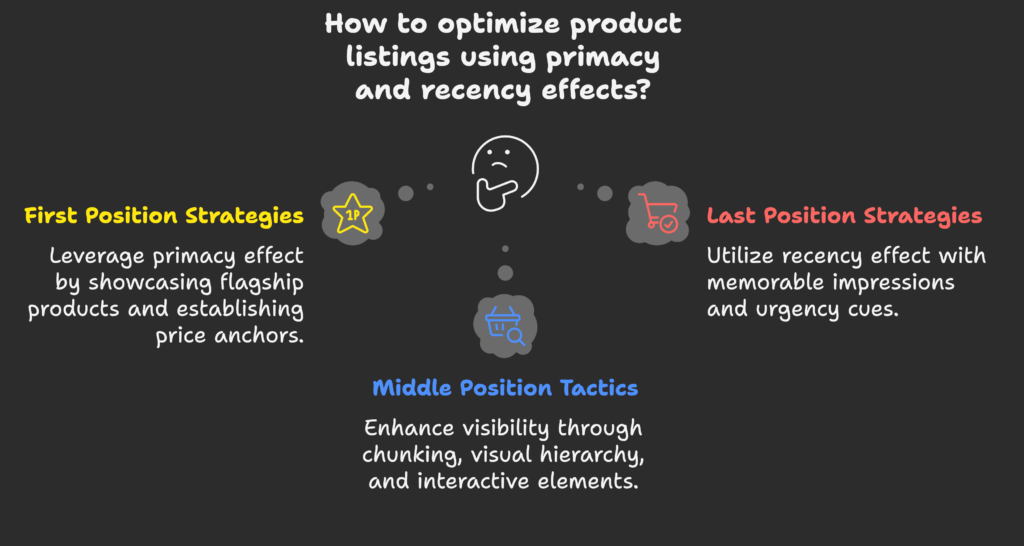
First Position (Primacy) Strategies
Items placed at the very start benefit from the primacy effect. Here’s how to make the most of that:
- Flagship or Premium Placement: Showcase your top-performing or premium items first to take advantage of heightened recall.
- Price Anchoring: Start with higher-priced or bundled products to make subsequent options look more affordable in comparison.
- Brand Building: Establish credibility by placing well-known or strongly branded items in the first slot, reinforcing authority.
- Perceived Value: Consumers often assume the first position signals importance—use it to highlight special features or benefits.
If the first position is all about making a bold statement, the last position is all about leaving a lasting impression. Let’s see how to leverage that next.
Last Position (Recency) Strategies
When people finish scrolling, the final products remain fresh in their minds. Use this recency effect to your advantage:
- Memorable Final Impression: Position eye-catching items or strong calls-to-action as the last thing users see.
- Cross-Selling & Upselling: Place complementary items at the end to prompt extra purchases right before checkout.
- Scarcity & Urgency: Features like “limited stock” or countdown timers are especially persuasive when positioned last.
- Footer Recommendations: Don’t waste your footer; include a “Recently Viewed” or “Recommended for You” section to close the deal.
First and last get the limelight, but what about everything in between? That’s where the real challenge—and opportunity—lives.
Addressing the Middle Position Challenge
The middle is often overlooked, but it doesn’t have to be. Try these tactics to shine a spotlight on middle listings:
- Chunking & Grouping: Divide your products into smaller sections with clear headings, creating new “starts” and “ends.”
- Visual Hierarchy: Use larger images or bold text to draw attention to middle items that might otherwise be skipped.
- Interactive Elements: Animations or hover effects can keep shoppers engaged long enough to remember middle items.
- Whitespace & Breaks: Strategic spacing helps reset users’ visual focus, so items in the middle don’t blend into the background.
With these strategies in mind, you’re poised to refine every aspect of your product listings. Next, let’s expand on how to implement them across different e-commerce contexts.
Implementation Across Different E-commerce Contexts
In this section, we’ll look at specific pages—category, search results, homepages, and even email campaigns—to see how the Serial Position Effect applies. By the end, you’ll know how to tailor your approach to each touchpoint for maximum impact.
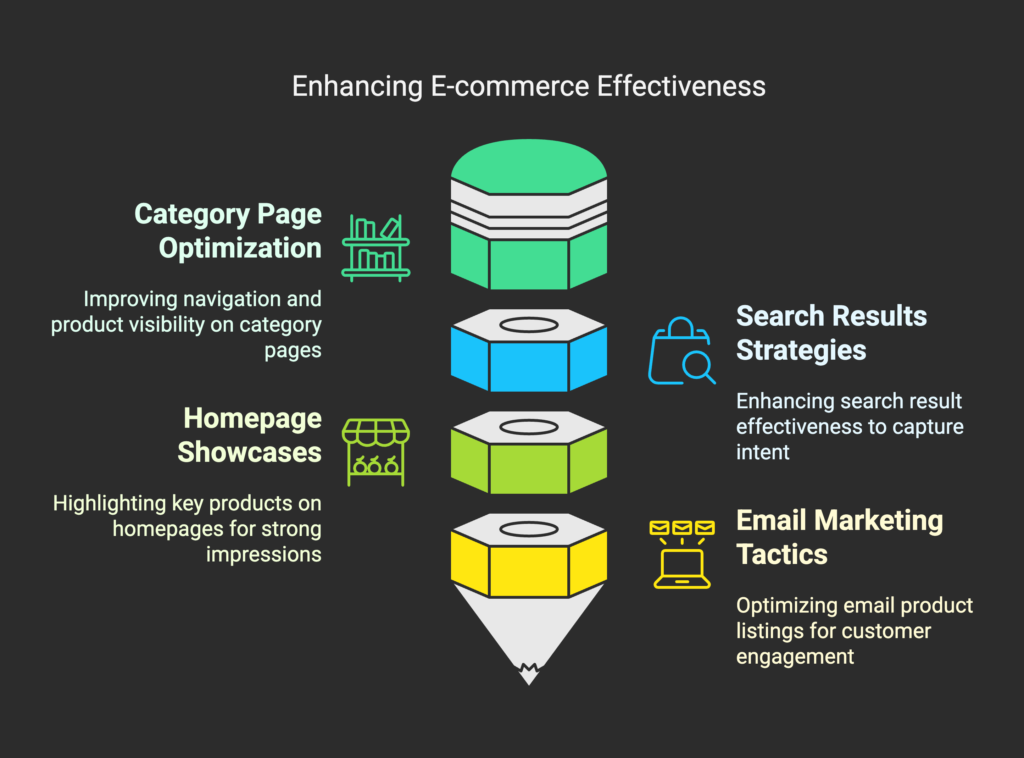
Product Category Page Optimization
Category pages are often the first stop for shoppers. Make it count by:
- Category Navigation Structure: Clear categories and subcategories help create multiple “first” positions for different groups.
- Featured Product Positioning: Highlight bestsellers or new arrivals at the top or bottom of each category page.
- Subcategory Organization: Use a logical flow, so shoppers naturally see key products at prime positions.
- Filter & Faceted Search: Pay attention to how filtering rearranges product listings. The top or bottom can shift dynamically.
Mastering category pages sets the tone for the rest of your site. Now let’s turn to search results, which often determine whether a shopper stays or leaves.
Search Results Page Strategies
When a shopper uses your site’s search function, they’re already showing purchase intent. Maximize the outcome with:
- Default Sort Order: Think carefully about whether you show “Best Match,” “Highest Rated,” or “Lowest Price” first.
- Sponsored Placements: Advertised products in the top or bottom slots catch the eye but must remain trustworthy.
- Hybrid Approaches: Combine relevance with the Serial Position Effect by sprinkling recommended items into prime spots.
- Mobile Optimization: Limited screen space means the first and last visible items are extra impactful on a phone.
From search results, shoppers often head to your homepage or landing pages to explore more. Let’s keep that momentum going.
Homepage and Landing Page Product Showcases
Your homepage is your storefront window. Make sure what stands out is truly memorable:
- Hero Section: Position a flagship product or promotion in the hero banner for a strong first impression.
- Featured Collections: Place bestsellers, seasonal items, or trending categories at the top or near the bottom for high recall.
- New Arrivals & Bestsellers: Mix these sections so that each set gets a chance to appear first or last on the page.
- Seasonal & Promotional Showcases: Use final page elements to remind visitors of current deals or upcoming sales.
Now, let’s see how these tactics apply to the less obvious but highly impactful realm of email marketing.
Email Marketing and Newsletter Product Listings
Emails can be a direct line to your customers. Leverage the Serial Position Effect here as well:
- Product Sequence Optimization: Start with an attention-grabbing offer and conclude with a strong call-to-action.
- Abandoned Cart Emails: Place the most compelling product (or biggest discount) at the top and a final nudge at the bottom.
- Post-Purchase Recommendations: Position items strategically to guide repeat purchases, using first and last slots for maximum recall.
- Template Design: Keep your template clean, ensuring the first and last products are visually prominent.
All these tactics sound promising, but how do you measure their success? In the next section, we’ll dig into testing and metrics.
Testing and Measuring Position Effect Impact
Now that you have a range of strategies, let’s discuss how to test them and measure results. By the end, you’ll know which metrics matter most and how to maintain continuous improvement.
A/B Testing Methodologies for Position Optimization
A/B testing is your best friend for validating changes:
- Split Testing Setup: Randomly divide traffic between two versions (e.g., different product orders).
- Controlling Variables: Keep as many factors identical as possible—only change product positions.
- Sample Size & Duration: Collect enough data to be statistically confident in your results.
- Segmentation: Test subsets of users to see if certain demographics respond more strongly to position changes.
With a good testing process in place, let’s look at the metrics that reveal whether your adjustments are succeeding.
Key Performance Metrics to Track
To understand if your efforts are paying off, focus on:
- Click-Through Rates (CTRs) by Position
- Conversion Rates for Items in Primacy and Recency Positions
- Average Order Value (AOV) Changes
- Add-to-Cart Rates in the Middle vs. Top/Bottom
- Heat Maps & Eye-Tracking for Visual Insights
Tracking these metrics consistently will show you where to refine your tactics. Up next is how to keep optimizing over time.
Continuous Optimization Frameworks
Position strategies aren’t a one-off project. They require ongoing attention:
- Iterative Testing: Regularly run experiments to adjust and refine positions based on new insights.
- Seasonal Adjustments: Product or shopper behavior can change during holidays, so stay agile.
- Competitive Analysis: Keep an eye on how rivals place products, and test improvements accordingly.
- Data-Driven Decisions: Rely on solid metrics to guide each tweak you make.
Ready to see how all this can go even further? Let’s explore advanced applications next.
Advanced Position Effect Applications
Feeling comfortable with the basics? Now we’ll layer on some more sophisticated methods, combining the Serial Position Effect with pricing psychology, personalization, and more. By the end, you’ll see how these advanced tactics can supercharge your store.
Psychological Pricing and Position Interaction
Position and price often go hand in hand:
- Price Anchoring: Place a high-priced item first to reframe subsequent prices as more affordable.
- Decoy Pricing: Insert a slightly less attractive option in the middle, making top or bottom choices more appealing.
- Bundle & Package Offers: Position bundles at the start or end to highlight savings.
- Discount Visualization: Display markdowns in the last position for a final, impactful push.
Next, we’ll see how personalization adds another layer of effectiveness.
Personalization and Position Effect
Tailoring positions to individual shoppers can drastically improve results:
- Dynamic Placement: Use browsing or purchase history to decide which items appear first or last.
- Behavioral Segmentation: Group users by their preferences, then adapt listings for each segment.
- AI-Driven Systems: Automated tools can rearrange products in real time to optimize for each visitor.
- Consistency vs. Adaptation: Strike a balance between personalizing positions and maintaining a predictable layout.
Beyond your own website, consider how to keep your strategies consistent across multiple channels. Let’s explore that now.
Cross-channel Position Consistency
If you sell on your own site and on marketplaces, consistency is key:
- Omnichannel Approach: Ensure product position strategies align across desktop sites, mobile apps, and physical stores.
- Mobile App Differences: Dedicated apps can offer more personalization, so track your position strategies carefully.
- Marketplace Tactics: Amazon and eBay often have their own algorithms, but you can still influence aspects like sponsored placements.
- Social Commerce: Platforms like Instagram Shops or Facebook Marketplace also have prime listing spots to consider.
Combine this with other psychological principles, and you’ll have a well-rounded strategy. Let’s see how that works.
Integration with Other Psychological Principles
Position is just one part of the puzzle:
- Scarcity: Pair “limited edition” messaging with first or last positions to intensify desire.
- Social Proof: Highlight reviews or star ratings in top or bottom positions for maximum impact.
- Authority: Use endorsements or certifications at the beginning to build credibility.
- Loss Aversion: Frame the middle items so that ignoring them seems like missing out.
Next, we’ll look at how these tactics have played out in real-world scenarios.
Case Studies and Practical Examples
Here, you’ll find real-life stories and research showcasing the power of strategic product positioning. You’ll also see how different industries tailor the Serial Position Effect to their unique markets. By the end, you’ll have concrete proof that these methods work.
E-commerce Success Stories
Some top online retailers saw conversion jumps by placing popular items first and high-margin items last. A clothing brand, for instance, tested reversing the default order of new arrivals, boosting sales by spotlighting its most lucrative lines. Smaller businesses also benefited by promoting bestsellers at both ends of a product list, making it easy for shoppers to remember and buy them.
Next, let’s see how the effect varies by industry.
Industry-Specific Applications
Every field uses the Serial Position Effect a bit differently:
- Fashion & Apparel: Featured outfits at the top attract quick attention, while sale items at the bottom trigger last-minute impulse buys.
- Electronics: High-end or flagship products often appear first to set a premium tone; bargain deals close out the list.
- Grocery & FMCG: Essentials at the start and indulgences at the end can help fill carts.
- Service-Based Listings: For bookings or services, prime and final slots can influence perceived quality and reliability.
Curious about academic validation? Let’s highlight some research next.
Experimental Research Findings
Studies confirm that placing products at the beginning or end of a listing increases recall and purchase likelihood. Eye-tracking research also shows consistent “hot spots” on category pages—often the top-left corner and the bottom area. Neuroscience hints that first and last items activate stronger emotional and memory-based responses.
It’s clear these tactics can work wonders, but we should also consider the ethical side. Let’s shift gears to that now.
Ethical Considerations and Limitations
While optimizing your listings is smart, it’s crucial to maintain trust and follow guidelines. By the end of this section, you’ll know how to balance strategy with transparency and accessibility.
Transparency and Consumer Trust
People appreciate honesty. Overdoing product manipulation can backfire if customers sense they’re being nudged unfairly. Disclosing sponsored positions clearly is often both ethical and legally required in many regions. Prioritize long-term trust over short-term gains.
Up next, let’s talk about making your strategies inclusive.
Accessibility and Inclusion Implications
Not everyone interacts with web content the same way:
- Cognitive Disabilities: Some users may not process lists in predictable ways, so keep important items accessible.
- Screen Readers: Make sure your site structure is screen-reader friendly, so the first or last items remain clear in audio form.
- Universal Design: Balanced layouts help all users navigate and recall key products.
Now, let’s briefly consider regulations that may influence your approach to product positioning.
Regulatory and Compliance Considerations
In some markets, there are guidelines on how sponsored or advertised items must be labeled. Stay informed on local rules, especially when operating internationally. By anticipating future regulations, you can keep your strategies compliant and trust-building.
With ethics covered, let’s jump to where the world of product positioning is heading next.
Future Trends in Position Effect Optimization
Wondering what’s next? Here, we’ll explore upcoming technologies, evolving consumer awareness, and new research angles that might reshape how we think about the Serial Position Effect.
Technological Developments
Innovation is moving fast:
- AI-Powered Positioning: Algorithms that adjust product order in real time based on user behavior.
- Predictive Analytics: Tools that guess which product will perform best in first or last position.
- AR/VR Shopping: In immersive experiences, “first” and “last” could be redefined by virtual layouts.
- Voice Commerce: Position might matter in the order items are read aloud by smart speakers.
As technology evolves, so do consumers. Let’s see how growing awareness shapes the future.
Evolving Consumer Awareness
Shoppers are increasingly savvy about marketing tactics. They may start recognizing patterns in how items are presented. Generational differences also come into play—some consumers might look specifically for middle items, knowing the common bias toward first and last.
Next, we’ll look at research frontiers that could unlock even more refined positioning methods.
Research Frontiers and Emerging Approaches
Expect to see more neuromarketing studies, cross-cultural comparisons, and explorations of how position strategies work in conjunction with broad UX principles. Long-term vs. short-term memory also remains an area of focus—some items may need repeated exposure to anchor in shoppers’ minds.
Curious to find out how to implement all this in a systematic way? Let’s move on.
Practical Implementation Guide
Time to put all these ideas into action. By the end of this guide, you’ll know exactly how to audit your site, plan improvements, and align your entire team for success.
Position Effect Audit Process
Start by taking a snapshot of your current listings:
- Assess Your Current Setup: Note where bestsellers, new arrivals, and promotional items are placed.
- Identify Opportunities: Look for items that deserve prime placement but are currently in the middle.
- Competitive Benchmark: Compare your approach with key competitors, noting what they do well.
- Prioritize Changes: Focus on areas with the highest potential ROI, like homepage banners or category tops.
Once you see where you stand, you can plan a roadmap for improvement.
Implementation Roadmap
A phased approach can help you roll out changes smoothly:
- Quick Wins: Simple moves like swapping top and middle items to test immediate gains.
- Medium-Term Plans: Redesign category pages or email templates to optimize the Serial Position Effect.
- Long-Term Strategy: Integrate AI-driven solutions for dynamic product ordering.
- Resource Allocation: Decide which teams or tools you’ll need for ongoing testing.
Finally, don’t forget to bring your team on board and make these principles part of your organization’s culture.
Team Training and Organizational Alignment
Everyone from your marketing to design team can benefit from understanding the Serial Position Effect:
- Education Sessions: Share key findings and show how strategic positioning can lift conversion rates.
- Cross-Functional Collaboration: Work with designers, developers, and copywriters to ensure consistent implementation.
- Embedding in Design Process: Make layout and positioning discussions a standard part of product page planning.
- Measuring Effectiveness: Regularly review metrics to see where training pays off and where more learning is needed.
With everyone aligned, you’ll be set for impactful changes. Let’s wrap up and summarize what you’ve learned.
Conclusion
Congratulations on making it to the end! You’ve explored a ton of information about the Serial Position Effect and its practical applications in e-commerce. Before you head off to optimize your listings, let’s recap the key points and outline some immediate next steps.
Key Takeaways
- The Serial Position Effect shows that shoppers remember first and last items best.
- Primacy and recency effects can both boost conversions when used strategically.
- Middle items shouldn’t be neglected—tactics like chunking and visual highlights can keep them visible.
- Continuous testing and adaptation are essential for long-term success.
Actionable Next Steps
- Immediate Audit: Check your store’s top and bottom product placements.
- Test & Measure: Run A/B tests focusing on first and last positions.
- Stay Informed: Keep up with new research on memory, attention, and UX design.
- Join Communities: Engage with forums or groups that discuss e-commerce and cognitive biases for fresh ideas.
By applying these strategies, you’ll keep refining how your products appear and remain in shoppers’ minds. And if you’re running a Shopify store, here’s a small reminder that you can boost sales even further by integrating tools like Growth Suite to optimize and streamline your entire operation.
References
- Venture Harbour. (2021, July 30). 7 Ways A Serial Position Effect Can Boost Conversions. Link
- Octet Design. (2025, February 28). What Is Serial Position Effect? Psychology And Examples. Link
- Career Foundry. (2021, August 5). What Is the Serial Position Effect? [With Examples]. Link
- AB Tasty. (2024, February 5). Using Serial Position Effect in UX Design. Link
- LogRocket Blog. (2025, January 28). Using the serial position effect in UX design. Link
- Baymard Institute. (2010, October 23). The Serial Position Effect in Web Design. Link
- Troyer, A.K. (2011). Serial Position Effect. In: Kreutzer, J.S., DeLuca, J., Caplan, B. (eds) Encyclopedia of Clinical Neuropsychology. Springer, New York, NY. Link
- The Decision Lab. (2021, October 11). Serial Position Effect – The Decision Lab. Link
- Glanzer, M., & Cunitz, A. R. (1966). Two storage mechanisms in free recall. Journal of Verbal Learning and Verbal Behavior, 5(4), 351-360.
- Murdock, B. B. (1962). The serial position effect of free recall. Journal of Experimental Psychology, 64(5), 482-488.
- Nielsen, J. (2006). F-Shaped Pattern For Reading Web Content. Nielsen Norman Group.
- Weinschenk, S. (2011). 100 Things Every Designer Needs to Know About People. New Riders.