Have you ever filled your online cart without even realizing it, or felt an unexpected rush of excitement when hitting the “Buy Now” button? Curious about why some purchases give you more satisfaction than others? In this article, you’ll uncover the fascinating world of neurotransmitters—especially dopamine, serotonin, and oxytocin—and how they shape our shopping habits. Ready to see why your brain lights up at a good sale? Let’s dive in!
In this section: We’ll explore how the shift from purely “rational” consumer models to neuroscience-based insights is transforming marketing and retail. You’ll learn about the D.O.S.E. framework—Dopamine, Oxytocin, Serotonin, and Endorphins—and see how these chemicals power everything from impulse buys to brand loyalty.
The Neurobiological Basis of Shopping Decisions
Once upon a time, economists believed we made decisions based only on logic and maximizing value. Now, we know our brains rely heavily on *emotions* and *neurochemistry*. Key areas in the brain—like the prefrontal cortex and the limbic system—join forces to influence what we buy. Understanding these neural processes can help companies optimize user experiences and help shoppers become more mindful of their choices.
The D.O.S.E Framework: Key Neurochemicals in Shopping Behavior
- Dopamine: Fuels our motivation and craving for rewards. It sparks excitement when we spot a good deal or anticipate a new product.
- Oxytocin: Often called the “love hormone,” it builds trust and loyalty, making us feel connected to certain brands or communities.
- Serotonin: Stabilizes our mood and contributes to feelings of contentment—important for satisfaction after buying something.
- Endorphins: Provide feelings of pleasure and can soothe stress. They may give us that cheerful rush during a fun shopping trip.
The Neuroscience Revolution in Marketing and Retail
Marketing has evolved from guesswork and intuition to neuromarketing, where brands use brain-imaging studies and psychological experiments to tailor everything from packaging design to ad campaigns. Research shows consumers are far more likely to choose a product if their dopamine pathways are activated, or if they’ve formed a strong oxytocin-based bond with a brand. This isn’t just theory—companies leveraging neuroscience see boosts in conversion rates and long-term customer loyalty.
We’ve introduced the bigger picture of how the brain drives shopping. Now, let’s zero in on the king of motivation: dopamine!
Dopamine: The Driver of Shopping Motivation and Reward
In this section: We’ll dive into dopamine’s role in fueling our desire to shop. You’ll see how browsing, buying, and even owning a product can trigger dopamine release, sometimes leading to impulse buys or even addictive patterns.
Neurobiological Mechanisms of Dopamine
Dopamine flows through various pathways in the brain. Two major ones are the mesolimbic (important for reward and pleasure) and the mesocortical (involved in planning and decision-making). The nucleus accumbens, often called the brain’s “reward center,” lights up when we anticipate getting something we want—like a new gadget on sale. Genetics also plays a part; certain people have variations in dopamine receptors, making them more prone to excitement or risk-taking behaviors.
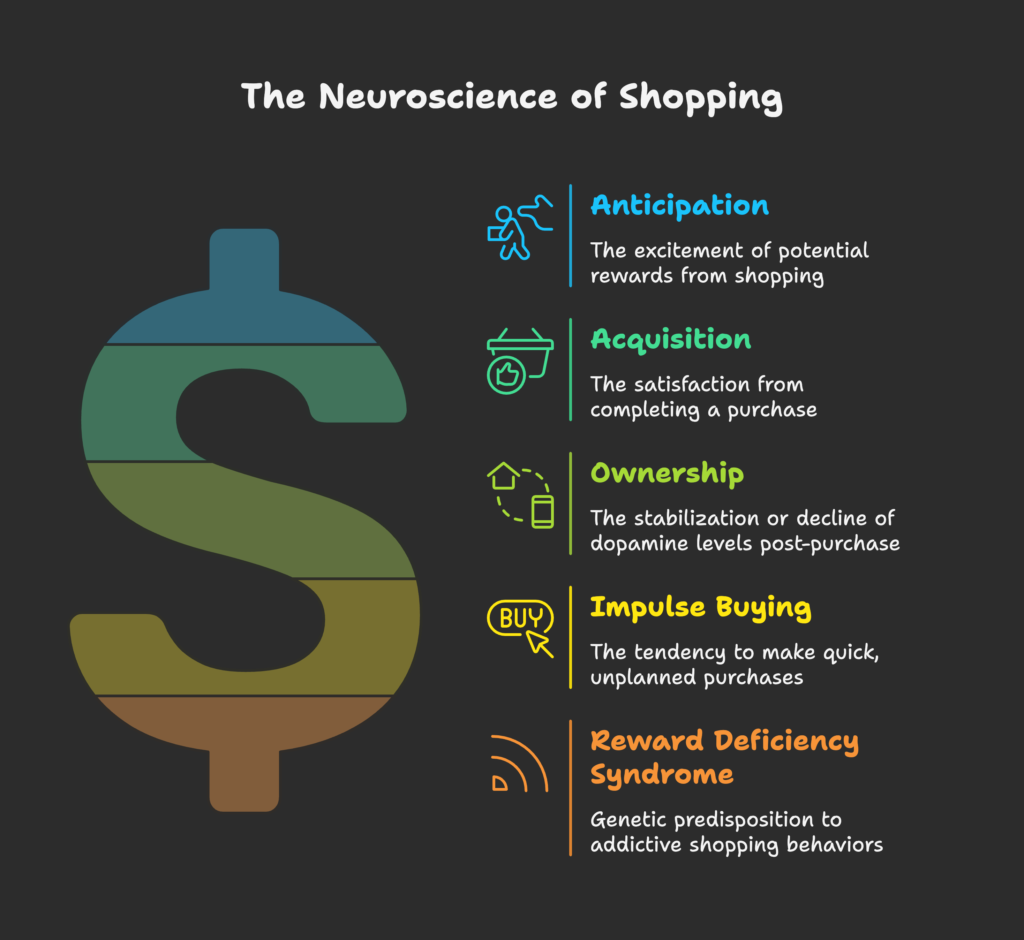
The Dopamine Shopping Cycle
- Anticipation: Just browsing a store or website can cause a spike in dopamine, as we imagine potential rewards.
- Acquisition: Completing a purchase gives us a *dopamine hit*, reinforcing the habit of buying.
- Ownership: After we get the item, dopamine levels may stabilize or drop, influencing whether we keep seeking new products.
Scientists using fMRI have found that the reward areas of the brain show heightened activity during these phases, confirming the powerful impact of dopamine on purchasing.
Dopamine and Impulse Buying Behavior
Ever wonder why you buy something on a whim, only to regret it later? Dopamine loves immediate rewards—so if the prefrontal cortex (which handles logical thinking) can’t keep up, you might click “Buy Now” impulsively. Sales countdowns and flash deals leverage this mechanism by increasing the sense of urgency, fueling dopamine-driven purchases.
Reward Deficiency Syndrome and Compulsive Shopping
Some individuals have what’s called a Reward Deficiency Syndrome—a genetic and neurochemical issue where their dopamine receptors don’t function normally. This can lead to shopping addiction as they constantly chase the “high” that dopamine gives. Studies show a link between certain genetic markers (like the DRD2 Taq A1 allele) and higher risk for compulsive behaviors, highlighting how biology can strongly influence shopping habits.
We’ve covered dopamine as the spark of desire. Next, let’s explore serotonin’s role in helping us feel satisfied and stable with our choices!
Serotonin: Stability, Satisfaction, and Shopping Experience
In this section: We’ll see how serotonin promotes contentment in consumer settings—why it helps us avoid post-purchase regret and how it can turn one-time buys into long-term brand loyalty.
Serotonin’s Neurobiological Function in Consumer Contexts
Serotonin is a mood regulator that calms anxiety and lifts our spirits. In the shopping realm, it keeps us from feeling overly stressed or regretful about spending money. For instance, someone with higher serotonin activity might experience less buyer’s remorse because they stay more balanced emotionally. Genetics plays a part here, too—some people have more efficient serotonin transporters, making them more resilient to stress.
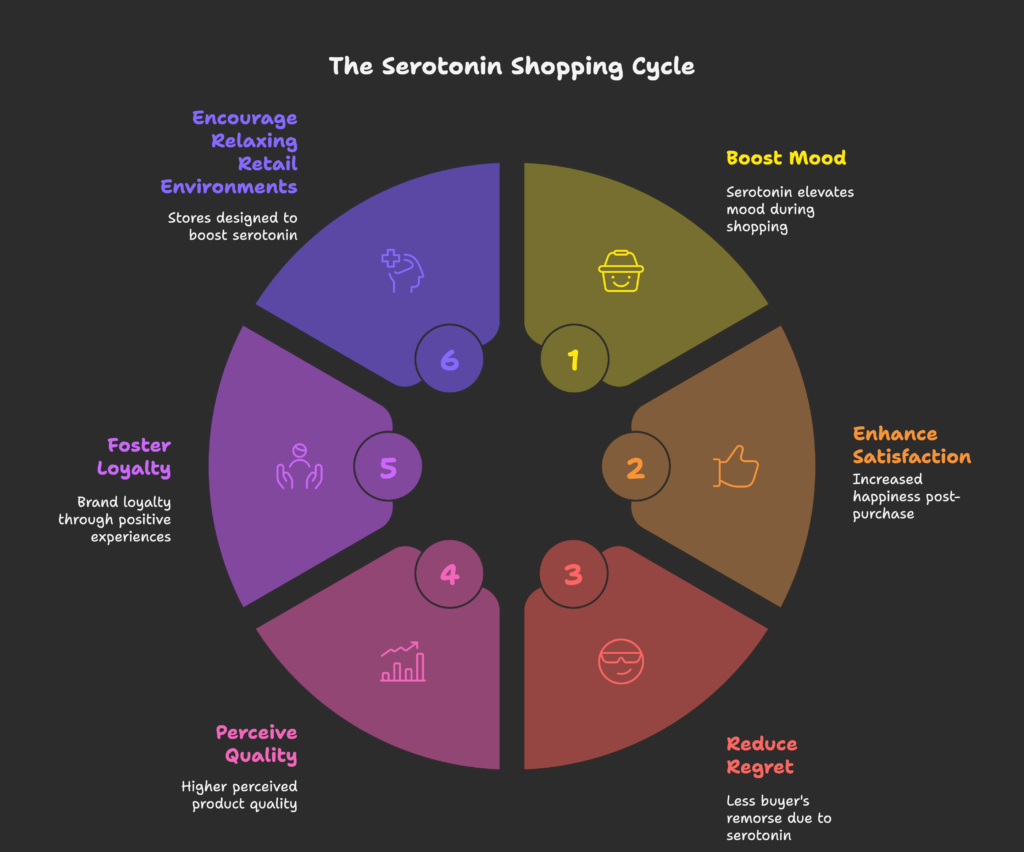
Serotonin’s Impact on Shopping Satisfaction
- Post-Purchase Glow: Serotonin can maintain a sense of happiness after we bring an item home.
- Reduced Buyer’s Remorse: Stable serotonin levels may help us accept our decisions without too much second-guessing.
- Quality Perception: When we feel good, we’re more likely to believe the product we bought meets our expectations.
Retail environments designed to be relaxing—soft music, comfortable lighting—help boost serotonin, encouraging a positive shopping vibe.
Brand Loyalty and Serotonin Activation
Have you ever felt loyal to a brand because it “just feels right”? That might be your serotonin at work. When we repeatedly have good experiences, our brains form a habit loop that’s reinforced by these calming, reassuring feelings. Some companies focus on making their customers feel secure—highlighting “better, safer, healthier” choices—which can elevate serotonin-based trust and routine shopping patterns.
Shopping as “Retail Therapy”: The Serotonin Connection
We’ve all heard of “retail therapy,” but why does shopping actually improve our mood? Research suggests that selecting and buying items can increase serotonin, at least temporarily, providing a small emotional lift. In healthy doses, this can be a harmless pick-me-up. The key is not crossing into excessive spending, where chasing that good feeling leads to financial problems.
We’ve learned about dopamine’s excitement and serotonin’s reassurance. Now let’s turn to oxytocin—the neurochemical that fuels trust and emotional bonds with favorite brands!
Oxytocin: Trust, Connection, and Social Shopping
In this section: We’ll explore how oxytocin—the “cuddle hormone”—impacts brand loyalty, social commerce, and customer trust. You’ll see why friendly store staff and community-driven marketing can create deep brand bonds.
Oxytocin Neurophysiology in Social Contexts
Oxytocin is released during positive social interactions, enhancing trust and reducing fear. In the brain, it works closely with the amygdala (which processes threats) to quiet skepticism. Factors like genetics and personal history can influence how much oxytocin we produce, but even small surges—like a friendly smile from a salesperson—can heighten our sense of comfort and belonging.
Building Brand Trust Through Oxytocin Activation
- Authentic Interactions: Genuine conversations (online or in person) can boost oxytocin levels, making customers feel welcomed.
- Reduced Risk Perception: Oxytocin helps us feel safer, so we’re more willing to try new brands or products.
- Service with Empathy: Empathetic customer service can generate oxytocin, fostering long-term loyalty.
Studies confirm that brands seen as caring and reliable spark higher oxytocin levels and deeper emotional ties than purely transactional ones.
Social Shopping and Oxytocin Release
Ever loved shopping with friends or discussing products in online groups? That sense of camaraderie partly arises from oxytocin. Human brains evolved to thrive in community settings—when we share experiences, our oxytocin levels go up. Retailers can create communal spaces, offer group-based deals, or host events to capitalize on this *social* chemical surge.
Oxytocin and Customer-Brand Relationships
Brands that tell compelling stories, champion customer success, or show genuine care about social causes can harness oxytocin. This hormone solidifies the emotional bonds that transform casual customers into brand advocates. Campaigns that celebrate community, charity, or personal growth often tap into this powerful neural mechanism, leading to higher engagement.
We’ve explored how dopamine, serotonin, and oxytocin each affect shopping. But these chemicals rarely act alone. Let’s look at how they interact to shape our total shopping experience!
Neurotransmitter Interactions and Shopping Behavior
In this section: We’ll discover how multiple neurochemicals work together in different phases of shopping, why some people react differently, and how this knowledge can be applied to enhance retail experiences.
The Neurochemical Cocktail of Shopping Experiences
Our brains rarely rely on just one neurotransmitter at a time. For instance, *dopamine and oxytocin* might interact if you’re excited about a new product *and* building trust with the store staff. A balanced mix of neurochemicals can create a satisfying customer journey—exciting yet comforting, and ultimately rewarding.
The Neurochemistry of Different Shopping Phases
- Browse Phase: Dopamine levels rise with curiosity, while a bit of serotonin helps keep stress in check.
- Decision Phase: Dopamine competes with rational thought, oxytocin can reduce fear, and serotonin steadies your mood.
- Purchase Phase: Dopamine peaks at the moment of buying; oxytocin might spike if you feel trust or community support.
- Post-Purchase Phase: Serotonin helps with contentment, while dopamine may drop unless you continue seeking new items.
Individual Differences in Neurochemical Response
Not everyone responds the same way. Genetics, age, personality, and health all shape how our brains produce or respond to these chemicals. For instance, a young adult high in sensation-seeking might get a strong dopamine rush from risky, limited-time offers, while a more cautious consumer might rely on serotonin for calm, careful shopping decisions.
Now that we understand these chemicals, how can businesses design experiences to optimally release them? Let’s explore strategies in store design, marketing, and beyond!
Retail Design and Marketing Strategies Based on Neurotransmitter Science
In this section: We’ll outline practical tactics to harness the power of dopamine, oxytocin, and serotonin in both physical and digital retail, and see how some brands successfully leverage these insights.
Creating Dopamine-Optimized Shopping Environments
- Store Layouts: Place high-interest items in surprising or visually appealing spots to spark curiosity.
- Digital Interfaces: Use engaging product photos, rewards, or gamification elements to stimulate small dopamine hits.
- Special Offers: Limited-time discounts or VIP deals act as *dopamine triggers* by adding excitement and urgency.
Oxytocin-Enhancing Customer Experience Strategies
Train your staff to greet customers warmly and listen actively. Offer shared experiences—like workshops or social media communities—where customers feel a sense of belonging. Use storytelling in your campaigns to create emotional resonance, boosting oxytocin. Trust signals, like secure payment icons or heartfelt testimonials, also reduce fear and encourage bonding.
Serotonin-Based Satisfaction Enhancement
- Calming Atmospheres: Soft music, pleasant scents, and gentle lighting can help maintain serotonin levels.
- Post-Purchase Outreach: Send follow-up emails that congratulate the customer on a good choice, reinforcing a sense of satisfaction.
- Quality Assurance: Warranties, easy returns, and transparent policies reduce anxiety, aligning with serotonin’s stress-lowering effect.
Multi-Neurotransmitter Marketing Frameworks
Some brands adopt a holistic “D.O.S.E” approach, ensuring all key neurotransmitters get positive stimulation: dopamine for excitement, oxytocin for trust, serotonin for contentment, and endorphins for feel-good moments. Case studies show that well-rounded campaigns can lead to higher conversions and stronger brand loyalty.
We’ve uncovered how to inspire healthy chemical responses. But with great power comes great responsibility. Let’s discuss the ethical side of neuromarketing!
Neuroethics and Consumer Protection
In this section: We’ll address the fine line between using neurotransmitter insights to offer better experiences and manipulating vulnerable shoppers. You’ll also discover how ethical considerations can guide responsible neuromarketing.
Ethical Considerations in Neurotransmitter-Based Marketing
While it’s tempting to maximize sales by tapping deep into our brain chemistry, companies must avoid deceptive or manipulative tactics. Clear disclosure that you’re using data to enhance experiences (rather than exploit weaknesses) is crucial. Marketers have a moral duty to protect groups who might be more susceptible—like those with mental health challenges or reward deficiency disorders.
Compulsive Shopping and Neurochemical Vulnerability
For some, *compulsive buying* can be as destructive as substance addiction. Retailers should be aware that certain practices—like constant flash sales—can exacerbate addictive tendencies. Responsible businesses monitor patterns to ensure they’re not pushing at-risk customers over the edge. Regulatory frameworks may evolve to address these concerns, aiming to protect the most vulnerable while still allowing normal marketing innovation.
Consumer Education on Neurochemical Influences
Empowering shoppers to recognize emotional triggers can help them make more informed decisions. Some forward-thinking brands offer tips on mindful shopping or even highlight how they aim to reduce stress (thus boosting healthy serotonin, for example). Greater transparency builds trust and fosters long-term relationships.
Now, let’s see how we actually measure all these brain chemicals in research and marketing contexts—and what the future holds in terms of technology and best practices!
Measurement and Research Methodologies
In this section: We’ll look at how scientists measure neurotransmitter activity through brain imaging, biochemical tests, and behavioral data. Understanding these methods clarifies which tactics genuinely influence buying decisions.
Neuroimaging Techniques for Studying Shopping Behavior
- fMRI (Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging): Shows which brain regions activate during shopping tasks.
- EEG (Electroencephalography): Tracks electrical brain signals in real time, useful for seeing immediate responses to ads or store layouts.
- Mobile Neuroimaging: Emerging technologies let researchers measure brain activity in more natural, everyday shopping environments.
Biochemical Measurement Approaches
Scientists can analyze saliva or blood samples for neurotransmitter byproducts like dopamine metabolites. Genetic testing can reveal predispositions for reward-seeking or stress responses. However, these methods have limitations (cost, privacy issues) and need to be applied carefully.
Behavioral and Psychological Assessment Methods
Not all marketers can run an fMRI lab! So simpler methods—like tracking shopper behavior via loyalty apps, conducting surveys that gauge mood, or using observational data—can offer practical insights. Some researchers use virtual reality simulations to standardize experiments while analyzing how participants respond in controlled, but realistic, shopping scenarios.
What does the future hold for neuroscience-based retail strategies? Let’s explore the next wave of technology, personalization, and therapy applications!
Future Directions and Emerging Research
In this section: We’ll peek into upcoming technologies in real-time neurotransmitter monitoring, personalized marketing based on brain chemistry, and potential therapeutic uses for shopping disorders.
Technological Advances in Neurotransmitter Research
- Real-Time Monitoring: Wearable devices that track changing neurochemical levels as you shop.
- AI-Based Prediction: Machine learning algorithms that predict dopamine spikes from certain product images or phrases.
- VR and AR: Virtual showrooms where researchers can precisely measure user reactions without real-world distractions.
Personalized Marketing Based on Neurochemical Profiles
Imagine receiving offers tailored to your unique dopamine or serotonin tendencies—this could boost satisfaction but also raises ethical questions. Could certain ads target people known to have lower impulse control? Regulation will likely grow around such personalized neuro-data. Done ethically, though, it might create truly satisfying shopping experiences for each individual.
Therapeutic Applications for Shopping Disorders
Compulsive shopping can devastate finances and relationships. As we learn more about the neurobiology of these disorders, solutions might include medication that stabilizes dopamine or digital tools that alert a user when they’re entering a high-risk impulse state. Neuroscience could also inform financial therapy sessions, helping people recognize and manage their emotional triggers.
Finally, we’ll wrap up with practical advice for anyone—brands or individuals—looking to harness these insights responsibly. Let’s check out our concluding section!
Conclusion and Practical Applications
In this section: We’ll summarize key takeaways about dopamine, serotonin, and oxytocin, offer an implementation roadmap for businesses, and reflect on how neurochemical understanding can shape the future of shopping.
Key Principles for Neurotransmitter-Informed Marketing
- Ethical Engagement: Influence without manipulating vulnerable shoppers.
- Balanced Neurochemical Activation: Combine dopamine excitement, oxytocin trust, and serotonin calm for better results.
- Clear Measurement: Track which methods work best via analytics, feedback, or smaller-scale neurological studies.
- Long-Term Relationships: Aim for sustainable, positive connections rather than short-term exploitation.
Implementation Framework for Businesses
Start by reviewing your current customer journey. Identify where you might add *dopamine-boosting* experiences (like exclusive deals), *oxytocin-building* activities (community events, empathetic service), and *serotonin-enhancing* strategies (stress-free returns, reassuring communication). Train your team to understand these principles so they can interact with customers more intuitively. Keep testing and refining until you find the ideal mix.
The Future of Neurotransmitter-Based Consumer Understanding
As neuroscience tech becomes more accessible, expect deeper insights into moment-by-moment changes in shoppers’ brains. Combined with traditional marketing knowledge, this could create more fulfilling shopping experiences—ones that respect consumers’ well-being while helping businesses thrive. Balancing a desire for profit with a commitment to positive experiences will be crucial. Ultimately, using neurochemical science responsibly can foster happier consumers, stronger brands, and a healthier marketplace.
Small Note: If you’re a Shopify store owner aiming to boost sales ethically and effectively, consider the Growth Suite application. It helps you guide your customers through dopamine-fueled discoveries, oxytocin-building interactions, and serotonin-enhancing follow-ups—all while maintaining a positive, trust-based relationship.
References
- Adcock Solutions. (2023). Elevate the Shopping Experience: Unleashing Dopamine, Oxytocin, Serotonin, and Endorphins
- Blum, K., et al. (2013). Neuro-Genetics of Reward Deficiency Syndrome (RDS). PubMed Central.
- Cleveland Clinic. (2025, March 6). Why ‘Retail Therapy’ Makes You Feel Happier.
- EWM. (2024, December 3). The Science Behind Impulse Buying.
- Knutson, B., et al. (2007). Neural predictors of purchases. PubMed Central.
- LinkedIn. (2024, December 21). How Sellers Can Harness The Power of Dopamine, Serotonin.
- Monk Prayogshala. (2023, November 6). The Neuroscience of Impulse Shopping.
- NeuroTracker. (2022, December 22). Why Shopping Makes you Feel High.
- NPR. (2010, July 30). Just Buy It: Impulsiveness Tied To Brain Chemical.
- Numerica Credit Union. (2024, December 17). Why we impulse buy — and how to stop.
- Pathmonk. (2023, October 23). Exploring the Neurological Roots of Consumer Behavior.
- Peltier, M. R., et al. (2018). Pro-dopamine regulator, KB220Z, attenuates hoarding and shopping behavior. PubMed Central.
- Pine, A., et al. (2010). Dopamine, Time, and Impulsivity in Humans. PubMed Central.
- Vespoli, L. (2023, September 8). Impulse Buying: The Neuroscience of Spontaneous Decisions. LinkedIn.



