Ever wondered why you get a little thrill when adding items to your online cart? Or why unboxing a new purchase feels so satisfying? Perhaps you’ve noticed that browsing your favorite store can lift your mood, even when you don’t buy anything?
If you’ve experienced any of these feelings, you’ve encountered the dopamine effect in shopping—a powerful neurological response that savvy businesses are increasingly using to create irresistible customer experiences.
Here’s something fascinating: it’s not actually the purchase itself that gives us the biggest pleasure hit—it’s the anticipation of it. That’s right! Your brain releases more dopamine (often called the “feel-good” neurotransmitter) during the hunt for products than when you actually acquire them. This revelation has completely transformed how forward-thinking businesses design their shopping experiences.
In this article, you’ll discover:
- Why your brain finds shopping so rewarding (even when your wallet doesn’t)
- How specific store designs and website elements trigger your brain’s reward system
- Practical strategies for creating anticipation that keeps customers coming back
- Real-world examples of brands that have mastered the art of dopamine-driven shopping
- How to measure and optimize the anticipation effect in your own business
- Ethical considerations to ensure you’re enhancing customer experience, not exploiting it
Whether you run an e-commerce store struggling with conversion rates, a physical retail space looking to increase foot traffic, or a service business aiming to create more engaging customer journeys, understanding the dopamine effect could be your secret weapon for growth. Let’s dive in!
Understanding the Dopamine Effect in Shopping
Before we dive into practical applications, let’s explore what’s actually happening in your customers’ brains when they shop. In this section, we’ll uncover the fascinating neuroscience behind shopping behavior and why it matters for your business.
The Brain Science Behind Shopping Pleasure
Shopping isn’t just an economic activity—it’s a neurological experience powered by specific brain chemicals:
- Dopamine is a neurotransmitter (a chemical messenger in your brain) that plays a central role in how we experience pleasure and motivation. It’s often simplistically called the “pleasure chemical,” but its true role is more about wanting and anticipating rewards than enjoying them
- When someone shops, their brain’s reward system activates, releasing dopamine into certain neural pathways
- Brain scanning studies show that simply viewing products we desire activates the nucleus accumbens, a brain region central to reward processing
- This neurological response explains why shopping can feel genuinely pleasurable on a biological level—it’s not just cultural conditioning
The numbers are compelling: fMRI studies demonstrate that browsing desirable products increases dopamine activity by 30-200%, depending on the individual and product category. This isn’t just an interesting science fact—it’s the biological foundation for billions of dollars in consumer spending.
The Surprising Truth: Anticipation Trumps Acquisition
Here’s the key insight that changes everything about effective retail design:
- Research has revealed that dopamine releases more strongly during the anticipation of a reward than during the reward itself
- This means the pleasure of shopping peaks during browsing, considering, and imagining—not at the moment of purchase
- This anticipatory pleasure has deep evolutionary roots—our ancestors who were motivated to pursue potential rewards (like hunting for food) had a survival advantage
- Digital commerce has dramatically amplified this effect by creating endless browsing possibilities, wishlists, and virtual shopping carts
This explains why window shopping can be enjoyable even without buying, why unboxing videos are so popular, and why the chase for limited-edition items creates such excitement. It’s all about the anticipation.
Why This Matters for Your Business
Understanding the dopamine effect offers tremendous business value:
- Conversion boost: Businesses that design for anticipation see conversion rate increases of 15-40% compared to those focused solely on transaction efficiency
- Customer retention: Creating positive dopamine loops can increase repeat purchase rates by up to 30%
- Competitive advantage: As markets become more crowded, neurologically optimized shopping experiences provide meaningful differentiation
- Higher ROI: Most anticipation-building tactics require minimal investment while yielding significant returns
The most successful businesses recognize that they’re not just selling products or services—they’re creating neurological experiences that customers crave and want to repeat.
Now that we understand what happens in the brain during shopping, let’s take a deeper look at the specific neural mechanisms that make anticipation so powerful. These insights will help us design shopping experiences that truly resonate with how our brains naturally work.
The Brain’s Shopping Reward System
To create truly effective shopping experiences, we need to understand the specific brain structures and chemicals involved in shopping anticipation. This section explores the neurobiological foundations that make shopping so rewarding—without getting too technical.
The Neural Pathways of Shopping Pleasure
Shopping activates several key brain regions that work together to create that “shopping high”:
- The ventral tegmental area (VTA) is like your brain’s reward generator—it produces dopamine when you spot something desirable
- The nucleus accumbens, sometimes called the brain’s “pleasure center,” receives dopamine signals and creates the sensation of wanting and anticipation
- These two areas form the mesolimbic pathway—the primary “desire circuit” that activates when customers browse products
- Meanwhile, the prefrontal cortex (your brain’s decision-maker) evaluates whether the anticipated pleasure is worth the cost
- The hippocampus records the entire experience, storing memories that influence future shopping behavior
Understanding these structures explains why browsing beautiful product displays feels good even when you don’t intend to buy—your VTA and nucleus accumbens activate regardless of whether a purchase occurs.
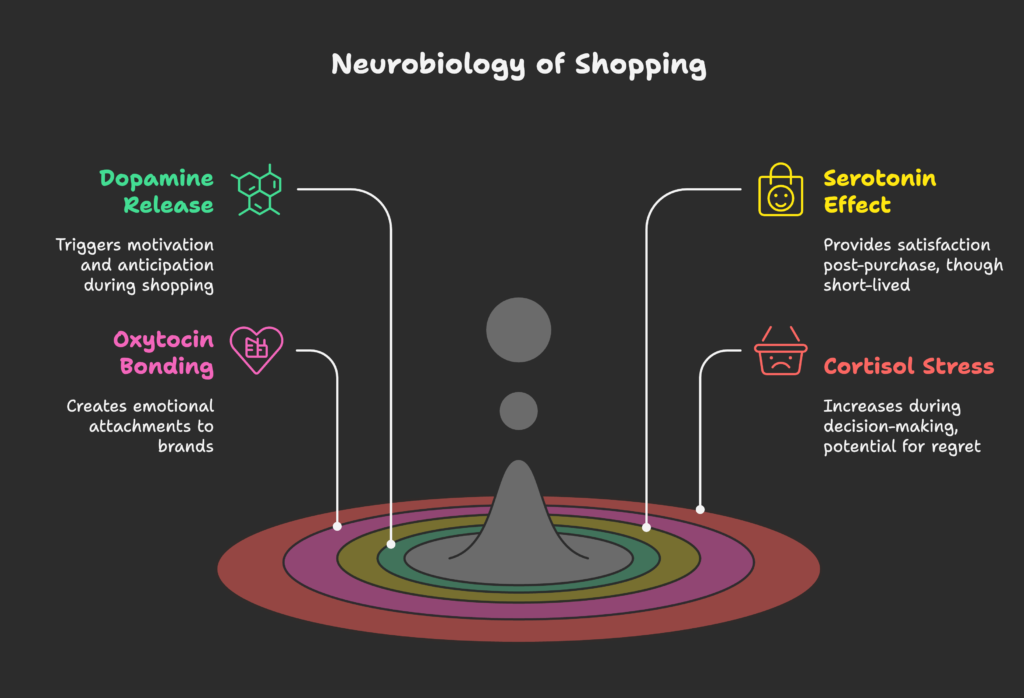
Shopping’s Chemical Cocktail
Shopping experiences trigger a symphony of neurotransmitters, each playing a different role:
- Dopamine creates the motivation and anticipation that drives shopping behavior—it spikes when you discover a potential purchase, see a sale, or imagine owning a product
- Serotonin contributes to feelings of satisfaction after a purchase (though this effect is typically shorter-lived than the anticipatory dopamine hit)
- Oxytocin, the “bonding hormone,” can create emotional attachments to brands that deliver consistently positive experiences
- Cortisol, a stress hormone, can increase during decision-making and may contribute to post-purchase regret if levels get too high
The balance between these chemicals helps explain the emotional roller coaster of shopping—from the excitement of discovery to the satisfaction of acquisition to the potential regret that sometimes follows.
What Brain Scans Reveal About Shopping Anticipation
Neuroscience research has provided fascinating insights into shopping behavior:
- fMRI studies show that brain activation begins before purchase—simply viewing desirable products lights up reward centers
- Dopamine release patterns show a distinct spike during browsing and consideration, with a smaller secondary release at the moment of purchase
- Interestingly, there are significant individual differences in these responses—some people naturally experience stronger dopamine reactions to shopping cues than others
- Memory systems play a crucial role in anticipation—past positive shopping experiences amplify dopamine response to similar future situations
These neurological patterns explain why effective shopping experiences aren’t just about the product itself but about the entire journey leading to acquisition.
The brain science is fascinating, but how does it translate into actual shopping behavior? Let’s explore the psychological mechanisms that connect these neurological responses to the shopping behaviors we can actually observe and influence.
The Psychology of Shopping Anticipation
Now that we understand the underlying brain mechanisms, let’s explore how they translate into shopping psychology. This section examines the mental and emotional processes that make anticipation such a powerful driver of shopping behavior.
How Expectations Shape Shopping Pleasure
The anticipation of reward involves several key psychological processes:
- Reward prediction is your brain’s way of forecasting how good something will make you feel—the more valuable the predicted reward, the greater the anticipatory pleasure
- Shopping involves constant risk-reward calculations—weighing the potential pleasure of acquisition against the pain of spending money
- Uncertainty plays a fascinating role—moderate uncertainty actually amplifies anticipatory pleasure (explaining why treasure-hunt shopping experiences like TJ Maxx are so engaging)
- Your brain constantly evaluates potential rewards based on past experiences, current desires, and imagined futures with the product
These prediction mechanisms explain why effective product descriptions and imagery that help customers imagine owning or using a product can be more persuasive than listing features alone.
The Emotional Journey of Shopping
Shopping creates a rich emotional landscape driven by anticipation:
- The thrill of the hunt is a genuine emotional state—searching for and discovering potential items triggers dopamine regardless of whether a purchase follows
- Desire intensifies through exposure—the more time spent considering a product, the stronger the anticipatory pleasure often becomes
- Anticipation creates positive emotional states including excitement, hope, and pleasurable tension
- The emotional arc from desire to acquisition includes multiple peaks and valleys that skilled retailers learn to choreograph
Understanding this emotional journey explains why customers often enjoy extended browsing experiences and why “sleeping on” major purchase decisions sometimes leads to increased desire.
Why Everyone Responds Differently
Not all shoppers experience anticipation identically—individual variations significantly impact shopping behavior:
- Genetic factors influence baseline dopamine sensitivity—some people naturally experience stronger reward responses than others
- Demographic differences appear in shopping anticipation—for example, research suggests younger shoppers often experience stronger novelty-seeking dopamine responses
- Personality traits like impulsivity and sensation-seeking correlate with different anticipatory shopping patterns
- Cultural background shapes what triggers anticipatory pleasure—the same shopping cues can generate different responses across cultures
These individual differences explain why segmentation is crucial in designing anticipatory shopping experiences—what creates pleasurable anticipation for one customer may not work for another.
Now that we understand the psychology behind shopping anticipation, let’s explore how retailers can apply these insights to create more engaging shopping environments. The retail design strategies in the next section translate these neurological and psychological principles into practical business applications.
Designing Retail Experiences That Trigger Dopamine
It’s time to turn theory into practice. This section explores how to apply our understanding of dopamine and anticipation to create shopping environments—both physical and digital—that naturally engage the brain’s reward system.
Physical Store Design for Maximum Anticipation
Brick-and-mortar retailers can strategically design spaces to enhance dopamine response:
- Layout strategies that encourage exploration reveal products gradually rather than all at once. This is why IKEA’s winding path and Sephora’s treasure-hunt layout are so effective at extending browsing time
- Sensory elements like ambient music, signature scents, and touchable displays engage multiple senses, amplifying dopamine response through sensory richness
- Display techniques like product spotlighting, staged vignettes, and limited-quantity presentations heighten desirability through visual cues
- Staff interactions can strategically build anticipation through storytelling about products, hinting at popular items, or creating FOMO (“this is selling out fast”)
Retailers like Apple masterfully apply these principles—products are displayed on open tables inviting touch, while new releases are sometimes kept slightly hidden behind curtains, building anticipation through mystery.
E-commerce Design That Triggers Reward Response
Online shopping environments can be specifically engineered to enhance anticipatory pleasure:
- Product page elements that boost dopamine include high-quality zoom features, 360° views, lifestyle imagery, and video demonstrations that help customers imagine ownership
- Navigation design can encourage exploratory browsing through recommendation engines (“you might also like”), curated collections, and discovery features
- Search functionality that reveals unexpected but relevant items creates the digital equivalent of treasure-hunting
- Strategic loading effects and animations can actually enhance anticipation—the brief suspense of a “revealing” animation can increase dopamine response to what follows
Amazon’s implementation of “frequently bought together” and “customers also viewed” features isn’t just about increasing basket size—it creates additional dopamine-triggering discovery moments throughout the shopping journey.
Creating Consistent Anticipation Across Channels
Modern shoppers move between channels, requiring cohesive anticipation strategies:
- Cross-channel consistency in anticipation triggers helps maintain dopamine engagement as customers switch between online browsing and in-store shopping
- Mobile-specific considerations include designing for shorter attention spans while maximizing visual impact and creating thumb-friendly exploration paths
- Online-to-offline journeys can be enhanced through features like online browsing with in-store pickup—combining digital exploration with immediate gratification
- Anticipation continuity can be maintained through consistent visual language, scent branding, and sound design across all touchpoints
Sephora exemplifies this approach by maintaining consistent anticipation triggers across their app, website, and physical stores—all featuring exploration-focused design, sample opportunities, and reward system visibility.
Store design creates the environment for anticipation, but marketing strategies actively build and amplify it. Let’s explore how effective marketing techniques can trigger dopamine release long before customers even enter the shopping environment.
Marketing Tactics That Build Anticipation
Beyond the shopping environment itself, marketing provides powerful tools for creating dopamine-triggering anticipation. This section explores strategies that build excitement and desire before customers even begin browsing.
Building Excitement Before Launch
Pre-launch campaigns can create powerful anticipation that drives both attention and sales:
- Teaser campaigns that gradually reveal product details activate curiosity and anticipation—Apple’s famous product event invitations exemplify this approach
- Strategic reveal sequencing can maximize dopamine response—releasing information in an intentional pattern creates multiple anticipation peaks rather than a single reveal
- Waitlist psychology leverages both exclusivity and anticipation—being “on the list” creates its own form of ownership anticipation
- Early access offers create tiered anticipation, with the fortunate few who get first access experiencing heightened dopamine response
Nike’s sneaker drops demonstrate this strategy perfectly—limited-edition releases are teased weeks in advance, creating extensive social media conversation and anticipation that translates to instant sellouts upon release.
Email and Notification Strategies
Direct communications can trigger powerful anticipatory responses:
- Subject line crafting for dopamine response involves creating curiosity gaps (“You won’t believe what’s coming next…”) or hinting at exclusive opportunities
- Sequential email campaigns can build anticipation through a series of revelations rather than a single announcement
- Push notification timing can be optimized to create anticipation peaks—messages about upcoming sales or restocks create pleasurable anticipation even before shopping begins
- Language patterns that trigger anticipation include phrases like “coming soon,” “be the first,” and “revealing tomorrow”—all signaling future rewards
Beauty subscription service Birchbox mastered this approach with their “sneak peek” emails revealing selected items from upcoming boxes, creating anticipation that subscribers report is sometimes more enjoyable than receiving the actual products.
Social Media Anticipation Building
Social platforms offer unique opportunities for creating contagious anticipation:
- Shareable anticipation content like countdown graphics, teaser videos, and “coming soon” announcements can spread anticipation virally
- User-generated anticipation occurs when customers share their excitement about upcoming products, creating social proof that amplifies others’ anticipatory pleasure
- Platform-specific strategies like Instagram countdowns, TikTok reveal videos, or Twitter teaser campaigns leverage each platform’s unique features
- Influencer collaborations can expand anticipation reach—influencers expressing excitement about upcoming releases transfer that anticipatory pleasure to their followers
Glossier’s product launches exemplify this approach—they seed early product information to dedicated fans who create anticipation-building content that spreads organically through beauty communities long before official release.
Marketing creates broad anticipation, but product and pricing strategies can enhance the anticipatory reward experience at a more specific level. Let’s explore how to build anticipation directly into your products, services, and offers.
Products and Pricing That Enhance Anticipation
The products themselves and how they’re offered can significantly impact dopamine response. This section explores how to design products, services, and pricing strategies that naturally create rewarding anticipation.
Designing Products for Anticipatory Pleasure
Thoughtful product design can enhance the anticipation experience:
- Unboxing experiences have become crucial for physical products—Apple’s precisely engineered packaging creates a multistep reveal that prolongs the anticipatory pleasure
- Progressive discovery features in products create extended anticipation—think of video games that gradually reveal new levels or features as players advance
- Anticipatory physical elements might include sealed compartments, hidden features, or transforming components that create a sense of revelation
- Digital product engagement can be designed with anticipation loops—revealing new capabilities or content as users engage more deeply
Luxury brands like Tiffany have perfected this approach—their signature blue box creates anticipation before it’s even opened, with multiple layers of packaging creating a prolonged revelation experience.
Pricing and Promotional Anticipation
Strategic pricing and promotional approaches can trigger powerful anticipatory responses:
- Limited-time offers create urgency-based anticipation—the countdown to a sale ending can trigger dopamine release through anticipation of potential savings
- Loyalty programs create ongoing anticipation through point accumulation and reward thresholds—the “almost there” feeling as customers approach reward levels is dopamine-driven
- Strategic bundling creates anticipation of enhanced value—”mystery box” offerings particularly leverage the anticipation of unknown but guaranteed rewards
- Flash sales with limited inventory create dual anticipation—both of the sale starting and the fear of missing out
Discount retailer Zulily has built their entire business model around this approach—daily deals create habitual checking behavior driven by anticipation of new offerings, while limited-time availability encourages quick decisions.
Extending Anticipation After Purchase
The anticipation window can extend beyond the purchase moment:
- Delivery tracking creates a post-purchase anticipation period—services like Domino’s pizza tracker leverage this by gamifying the wait time
- Post-purchase communications can maintain engagement through “your order is being prepared” updates or “tips to prepare for your item’s arrival”
- Review solicitation can be framed as anticipation fulfillment—”Share your experience with others who are considering this purchase”
- Next purchase anticipation can begin immediately—”Based on this purchase, you might enjoy…” recommendations create a new anticipation cycle
Fashion subscription service Stitch Fix epitomizes this approach—the period between ordering and receiving a “fix” is filled with anticipatory communications, while each delivery includes teaser cards about potential future selections.
While strategic pricing and product design can create powerful anticipation, gamification takes these principles even further by explicitly designing reward anticipation into the shopping experience itself. Let’s explore how game mechanics can create shopping experiences that are literally addictive to the brain’s reward system.
Gamification: Turning Shopping Into a Dopamine-Triggering Game
Gamification—the application of game elements to non-game contexts—provides powerful tools for creating dopamine-driven shopping experiences. This section explores how to integrate game mechanics that naturally trigger reward anticipation.
Creating Addictive Reward Systems
Strategic reward structures can create ongoing anticipation and engagement:
- Progress tracking mechanisms like visual progress bars or milestone markers create anticipation of achievement—Starbucks’ reward level system exemplifies this approach
- Point accumulation systems work because they create continuous small anticipation triggers—each purchase brings you closer to a reward threshold
- Achievement unlocking creates surprise dopamine hits—unexpected badges or status levels for reaching certain milestones provide unscheduled rewards that are particularly effective
- Effort-reward balancing is crucial—rewards that require some effort create stronger anticipatory pleasure than easily obtained ones
Sephora’s Beauty Insider program demonstrates these principles perfectly—point accumulation, visible progress to the next tier, and surprise rewards create multiple anticipation streams that drive ongoing engagement.
Creating Game-Like Shopping Experiences
Shopping itself can be transformed into an engaging game:
- Gamified checkout experiences might include “spin to win” discounts or surprise gift offerings that create anticipation at the crucial conversion moment
- Treasure hunt shopping designs like those used by TJ Maxx or HomeGoods create exploration-based anticipation—you never know what you might find
- Interactive shopping games such as Alibaba’s “Catch the Cat” game during Singles’ Day create playful anticipation separate from the products themselves
- Contest integration like instant win opportunities or scratch-off virtual cards create microburst anticipation moments
Cosmetics retailer Ulta has experimented with various gamification approaches, including their “Beauty on the Go” challenge that rewards store visits with points and surprise perks, creating anticipation that drives foot traffic.
The Power of Social Competition
Social elements can significantly amplify gamification’s anticipatory effects:
- Leaderboards and rankings create social comparison anticipation—seeing yourself climb rankings triggers dopamine even before any tangible reward
- Group goals and challenges create shared anticipation—”If 1000 people participate, everyone gets X” creates collective anticipatory pleasure
- Social shopping events like exclusive member sales or virtual shopping parties create anticipation through scheduled social experiences
- Community challenges with shared rewards create both individual and group anticipation loops
Peloton masterfully leverages social competition with their leaderboards and community challenges, creating anticipation not just of exercise results but of social recognition and achievement.
Implementing these strategies is just the beginning—measuring their effectiveness is crucial for optimization. Let’s explore how to track and improve the dopamine-triggering elements in your shopping experience.
Measuring and Optimizing Anticipation Effects
Implementing anticipation strategies is only effective if you can measure their impact and continuously improve them. This section explores practical approaches to tracking, testing, and enhancing dopamine-driven shopping experiences.
Metrics That Matter for Anticipation
Several key indicators can help you assess anticipation effectiveness:
- Engagement metrics for anticipatory content like email open rates for teaser campaigns, video completion rates for reveal content, or dwell time on coming-soon pages
- Neurological measurements are becoming more accessible through tools like facial expression analysis, eye tracking, and even consumer-grade EEG headsets for larger operations
- Conversion impact should be tracked through careful A/B testing of pages with and without anticipation elements
- Lifetime value effects of anticipation strategies can be assessed by cohort analysis comparing customers acquired through high-anticipation versus standard pathways
The most sophisticated retailers combine these metrics to create anticipation effectiveness scores for different strategies, allowing for data-driven optimization.
Testing Approaches for Dopamine Strategies
Systematic testing reveals what actually works for your specific audience:
- A/B testing frameworks should specifically isolate anticipation elements—compare identical offers with different reveal mechanics or anticipation language
- User research techniques like facial coding during unboxing experiences or moderated shopping sessions can reveal emotional responses that metrics might miss
- Behavioral tracking through heat maps, session recordings, and click pattern analysis can reveal how customers interact with anticipation-building elements
- Qualitative assessment through post-purchase surveys specifically addressing the anticipation phase can provide valuable subjective feedback
Subscription beauty brand Birchbox extensively tests different “sneak peek” approaches for their monthly boxes, measuring not just click-through rates but also social sharing and community discussion volume to optimize anticipation.
Building Continuous Improvement Systems
Creating systematic approaches to optimization ensures ongoing enhancement:
- Iterative refinement cycles should be established with regular reviews of anticipation performance data
- Cross-functional collaboration between marketing, UX design, merchandising, and analytics teams ensures comprehensive optimization
- Competitive analysis of other brands’ anticipation strategies provides inspiration and benchmarking
- ROI assessment of anticipation investments should compare costs to both immediate conversion improvements and lifetime value enhancements
Fashion retailer ASOS demonstrates this approach with their regular testing of product reveal sequences on category pages, continuously optimizing the balance between showing enough to create interest without revealing so much that anticipation is diminished.
While the dopamine effect offers powerful business benefits, it also raises important ethical questions. Let’s explore how to create anticipatory experiences that enhance customer satisfaction without crossing into manipulation.
Ethical Considerations: The Responsibility of Triggering Dopamine
The power to trigger dopamine responses comes with significant ethical responsibilities. This section explores potential concerns and approaches to creating anticipatory experiences that benefit both businesses and customers.
Recognizing Potential Downsides
Several concerns merit careful consideration:
- Addiction potential: Shopping can become genuinely addictive for some individuals when dopamine triggers are extensively employed—research suggests approximately 6% of the population may be vulnerable to shopping addiction
- Financial wellbeing: Anticipation-driven purchases can lead to spending beyond means, particularly when combined with easy credit
- Post-purchase negativity: If anticipation is built too high, the actual product may disappoint, leading to returns, negative reviews, and customer dissatisfaction
- Emotional manipulation: Some anticipation tactics may cross the line from enhancement to exploitation, particularly when targeting vulnerable populations
These concerns don’t invalidate anticipation strategies but highlight the need for thoughtful, responsible implementation.
Creating Balanced Approaches
Several principles can guide ethical anticipation design:
- Sustainable anticipation creates experiences that remain rewarding over time rather than leading to diminishing returns or regret
- Transparency about what customers can realistically expect helps maintain trust even while creating excitement
- Financial wellbeing support might include clear return policies, responsible credit options, or even gentle “are you sure?” checkpoints for larger purchases
- Trust-building approaches ensure anticipation is followed by genuine satisfaction—the product or service should live up to the excitement created
Patagonia exemplifies ethical anticipation design—they create desire for their products while encouraging responsible consumption, even famously running a “Don’t Buy This Jacket” campaign asking customers to consider whether they truly need new items.
Navigating the Regulatory Landscape
The legal and industry context for anticipation strategies continues to evolve:
- Current regulations around persuasive design vary significantly by region but are generally increasing in scope
- Industry self-regulation opportunities exist through trade associations and shared best practices
- Cultural differences in what’s considered acceptable anticipation-building vary widely—approaches that work in one market may be viewed negatively in another
- Future-proofing strategies involve staying ahead of regulatory trends by adopting ethical approaches before they become mandated
Forward-thinking businesses recognize that ethical approaches to anticipation design aren’t just morally sound but make good business sense in an era of increasing consumer awareness and regulatory scrutiny.
Looking to the future, anticipation strategies continue to evolve with new technologies and changing consumer expectations. Let’s explore emerging trends and innovations that will shape the next generation of dopamine-driven shopping experiences.
The Future of Shopping and Dopamine: Emerging Trends
The landscape of anticipation-driven shopping continues to evolve rapidly. This final section explores emerging technologies and trends that will shape how businesses create dopamine-triggering experiences in the coming years.
Technology-Enabled Anticipation Experiences
New technologies are creating novel anticipation possibilities:
- AI personalization is enabling increasingly individualized anticipation experiences—algorithms can predict which specific products will create the strongest dopamine response for each customer
- Virtual and augmented reality create immersive anticipation experiences—virtual try-on technologies allow customers to preview products in their own environments, creating powerful ownership anticipation
- Voice commerce presents unique anticipation design challenges and opportunities—creating auditory anticipation cues without visual elements
- Internet of Things (IoT) integration enables connected products to create anticipation through smart notifications and predictive features
Furniture retailer IKEA is pioneering these approaches with their AR app that lets customers visualize products in their homes before purchase, creating a new form of ownership anticipation that significantly increases purchase confidence.
Neuroscience Advancements
Our understanding of the brain’s shopping behavior continues to develop:
- New research findings regularly refine our understanding of anticipation mechanisms—recent studies have begun mapping individual differences in dopamine response patterns
- Measurement technologies are becoming more accessible—consumer-grade EEG and biometric tools are making neuroscience insights available to more businesses
- Personalization based on neural profiles may soon allow experiences tailored to individual dopamine sensitivity
- Predictive modeling of anticipatory effectiveness continues to improve, allowing more precise design of anticipation triggers
Major retailers like Walmart and Amazon are investing heavily in consumer neuroscience research, suggesting that neurologically optimized shopping experiences will become increasingly sophisticated.
Evolving Consumer Attitudes
Customer expectations and awareness continue to shift:
- Increasing awareness of persuasive techniques means consumers are becoming more discerning about anticipation tactics
- Generational differences in response to anticipation strategies are significant—Gen Z shows greater skepticism toward traditional approaches while engaging deeply with authentic experiences
- Physical-digital balance expectations continue to evolve—post-pandemic shoppers increasingly seek seamless anticipation experiences that bridge online and offline
- Cultural evolution of anticipation expectations varies globally—effective approaches must be culturally attuned
These evolving attitudes suggest that future anticipation strategies will need to be more transparent, authentic, and value-adding rather than merely manipulative.
Conclusion: Crafting Dopamine-Driven Shopping Experiences
The dopamine effect in shopping represents one of the most powerful tools available for creating engaging, memorable customer experiences. By understanding and thoughtfully applying the principles of anticipation, businesses can create shopping journeys that are not only more profitable but genuinely more enjoyable for customers.
The key insights we’ve explored include:
- Dopamine releases more strongly during anticipation of rewards than during the reward itself
- Both physical and digital shopping environments can be designed to trigger anticipatory pleasure
- Marketing, product design, pricing, and gamification all offer opportunities to create anticipation
- Measurement and continuous optimization are essential for maximizing anticipation effectiveness
- Ethical considerations should guide the application of these powerful psychological principles
The most successful businesses recognize that they’re not just selling products or services—they’re creating neurological experiences that customers find genuinely rewarding. When done ethically and thoughtfully, anticipation-focused shopping design can create that rare win-win: more profitable businesses and more satisfying customer experiences.
As you apply these principles to your own business, remember that the goal isn’t manipulation but enhancement—creating shopping journeys that respect customers while delivering the anticipatory pleasure that makes shopping truly enjoyable.
Looking to implement these dopamine-triggering strategies in your Shopify store? The Growth Suite application helps merchants create anticipation-rich shopping experiences through teaser campaigns, gamified rewards, and strategic product reveals—all designed to boost conversion rates by engaging your customers’ natural reward systems.
References
- Semantic Scholar. (2025). Analyze the Influence of Positive Feedback to Declarative Memory Strength.
- NCBI. (2016). Reward Anticipation Dynamics during Cognitive Control and Episodic Encoding: Implications for Dopamine.
- NeuroTracker. (2022). Why Shopping Makes you Feel High.
- Interac. (2023). Your Brain on Shopping.
- Cleveland Clinic. (2025). Why ‘Retail Therapy’ Makes You Feel Happier.
- Regenesys. (2023). The Power of Dopamine: Understanding Its Influence on Spending Behaviour.
- GIPS Hospital. (2024). Understanding the Anticipatory Dopamine Theory: A Layman’s Guide.
- LinkedIn. (2024). The Role of Dopamine in the Buying Process.
- PubMed. (2018). Dopamine Transporter and Reward Anticipation in a Dimensional Perspective: A Multimodal Brain Imaging Study.
- NCBI. (2024). Chronic stress deficits in reward behaviour co-occur with low nucleus accumbens dopamine activity during reward anticipation.