Have you ever felt tempted to buy something just because it was labeled “limited edition” or “only a few left”?
Do you wonder why these messages are so powerful, yet sometimes leave buyers feeling tricked?
In this article, you will discover how to use scarcity and urgency in an honest, ethical way.
By reading this, you’ll learn why scarcity can be both effective and trustworthy, how to avoid manipulative tactics, and how to respect your customers while still improving sales.
Ready to explore how you can boost your conversions without any shady tricks? Let’s jump right in!
Introduction to Scarcity in Marketing
In this section, we’ll clarify what scarcity marketing is, how it relates to urgency, and why it’s been so widely used throughout history.
We’ll also explore how modern digital platforms have changed the way scarcity works. By the end, you’ll see a clear picture of scarcity’s role in marketing today and be ready to dive deeper into ethical considerations.
Defining Scarcity and Urgency
Scarcity marketing means creating a feeling that products, offers, or opportunities are in short supply.
When consumers believe something is limited, they tend to act faster because they fear missing out.
This sense of urgency is powered by our natural response to limited time or limited quantity.
Historically, merchants used signs like “Only a few items left” to drive attention.
Today, digital stores use similar tactics, such as countdown timers and stock displays, to prompt quick decisions.
We’ve uncovered the basics of scarcity and urgency.
But why do ethical approaches matter so much in this fast-moving digital era? Let’s find out next.
The Business Case for Ethical Urgency
Using scarcity in a fair and genuine way offers real business value.
Studies show that consumers feel more loyal to brands they trust, and trust is built when marketing claims match reality.
When people know you’re not tricking them, they are more likely to return for future purchases.
On the other hand, brands that rely on manipulative scarcity risk damaging their reputation.
In the long run, that can lead to lost sales, negative reviews, and a tarnished brand image.
So far, we see that honest urgency fosters trust and loyalty.
But how do we define where persuasion ends and manipulation begins? We’ll explore that next.
The Ethical Spectrum of Scarcity Tactics
Ethical scarcity puts transparency first. You make it clear why your offer is limited, and you let customers decide freely.
Unethical scarcity, however, pressures people using false claims or exaggerated limitations.
When you respect your customers’ freedom to make informed decisions, you nurture emotional security in the buying process.
That leads to happier, more satisfied buyers who stick around long-term.
We’ve now learned what’s acceptable and what’s not.
Next, let’s explore the psychology that explains why scarcity and urgency have such a strong pull on our minds.
The Psychology Behind Scarcity and Urgency
In this section, we’ll dive into how scarcity shapes the way people think, feel, and act.
We’ll look at the mental shortcuts that guide quick decisions and the emotional triggers that make limited offers irresistible.
By understanding these psychological elements, you’ll be better equipped to craft ethical scarcity tactics.
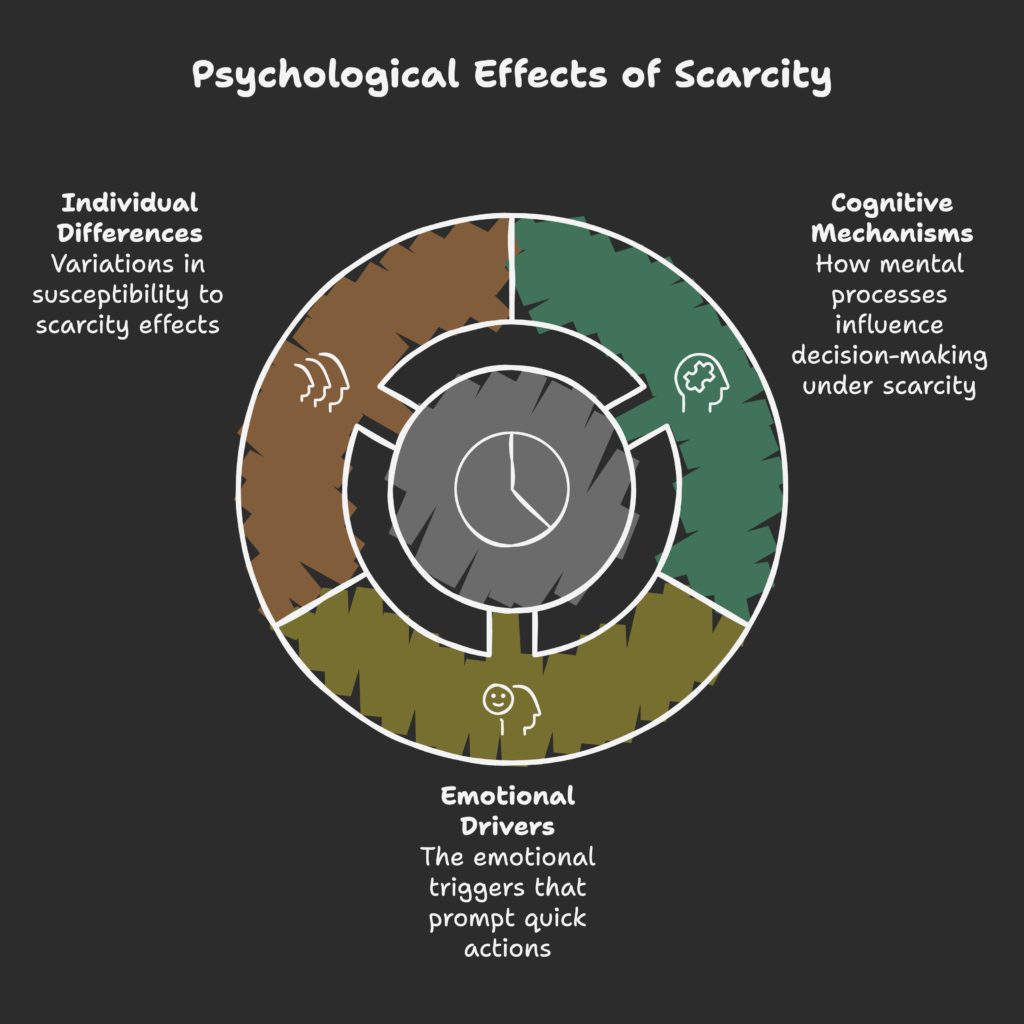
Cognitive Mechanisms
Humans tend to avoid losses more than they seek gains. This is called loss aversion, and it drives us to act quickly when something might vanish soon.
We also assign higher value to items we think are scarce, which can lead to impulsive choices.
Time pressure boosts this effect, making people rely on mental shortcuts (“If it’s almost gone, it must be worth it!”).
Curious how emotions like fear or excitement also play a part in this? Let’s uncover that next.
Emotional Drivers
Fear of Missing Out (FOMO) is a powerful trigger. No one wants to be left behind while others enjoy a special deal or unique product.
This sense of possible regret creates anxiety, prompting quick purchasing decisions.
At the same time, exclusivity can make buyers feel special, appealing to a desire for status or uniqueness.
When they actually get that limited item, they often experience a sense of relief and victory.
Emotions can be strong, but not everyone reacts the same way. So, how do factors like personality or culture change the impact of scarcity? Let’s see.
Individual Differences in Susceptibility
Some shoppers are more responsive to urgency than others. Younger audiences might be more used to flash sales online, while older adults may be more cautious.
Culture also plays a part: in some regions, high-pressure selling is normal; in others, it’s frowned upon.
Brands should be mindful of vulnerable groups, such as people on tight budgets or those with certain personality traits, to avoid exploitative practices.
Now that we’ve looked at how scarcity impacts the human mind, let’s shift to the ethical questions that come up when using these tactics.
The Ethics of Scarcity Marketing
Here, we’ll outline the main moral challenges of scarcity marketing, show examples of manipulative tactics to avoid, and discuss the guidelines from regulators.
By the end, you’ll know exactly what ethical boundaries look like and how to stay within them.
Common Ethical Concerns
There’s a thin line between motivation and manipulation.
Genuine scarcity is fine if the product or offer is truly limited.
But false claims (“Only 3 left!” when there are actually hundreds) are unfair to customers.
It can also harm vulnerable groups more severely, creating panic instead of informed decision-making.
Honesty and authenticity should always be your core guiding principles.
So, what do manipulative practices look like in real life? Let’s highlight some red flags next.
Identifying Manipulative Practices
- Fake countdown timers: Timers that reset when the page is refreshed create false urgency.
- False limited stock claims: Saying “Only 5 in stock” when you have plenty is misleading.
- Perpetual “limited time” offers: If the sale never ends, you’re not being honest.
- Misleading exclusivity: Claiming something is “VIP only” when anyone can get it.
Breaking these rules can lead to legal trouble. Next, let’s see how regulators look at such tactics.
Regulatory and Compliance Considerations
The Federal Trade Commission (FTC) in the United States, for example, warns against deceptive practices, including fake scarcity claims.
Many industry groups also promote self-regulation to keep marketing transparent.
In international markets, rules can vary, but the general principle remains the same: don’t lie to your customers, and don’t cause them harm.
Staying compliant shows that you respect and value your audience.
Ready to create ethical scarcity in your own campaigns? Let’s move to a framework that makes it possible.
Framework for Ethical Scarcity Implementation
Now we’ll discuss the core principles you need for honest urgency, show you how to adopt a trust-based approach, and explore ways to balance your business goals with consumer well-being.
This section will give you practical guidelines to stay on the right side of ethics.
Core Ethical Principles
- Honesty: Always be truthful about deadlines, stock, and availability.
- Respect: Give people room to make decisions without pressure.
- Value-based Urgency: Focus on why the offer is special, not just on fear.
- Consistency: Ensure your claims match reality (e.g., if time is up, end the promotion).
Keep these values in mind, and you’re halfway there. Next, we’ll see how to grow trust even before starting a scarcity campaign.
The Trust-Based Approach
Building credibility early makes your scarcity tactics more believable.
If people already see you as honest, they’ll accept your limited-time or limited-stock messages as genuine.
Concentrate on creating real value in your products or services, and let scarcity highlight that value instead of replacing it.
This approach leads to long-term relationships, not just one-off sales.
Balancing your need for profits with respect for customers is key. Let’s see how to strike that balance.
Balancing Business Needs with Consumer Respect
You can still set ambitious sales goals while respecting buyers. For instance, use real deadlines and set promotions that benefit both sides.
Applying ethical decision-making (like checking if your claims are true at each step) helps ensure your campaign feels fair.
Track not only conversion rates but also customer satisfaction to measure success fully.
With these principles in place, it’s time to learn about actual tactics you can apply to your business.
Ethical Scarcity Strategies in Practice
We’ll now explore clear examples of ethical urgency you can use right away.
From limited-time offers to exclusive access, each strategy will show you how to keep it real and fair.
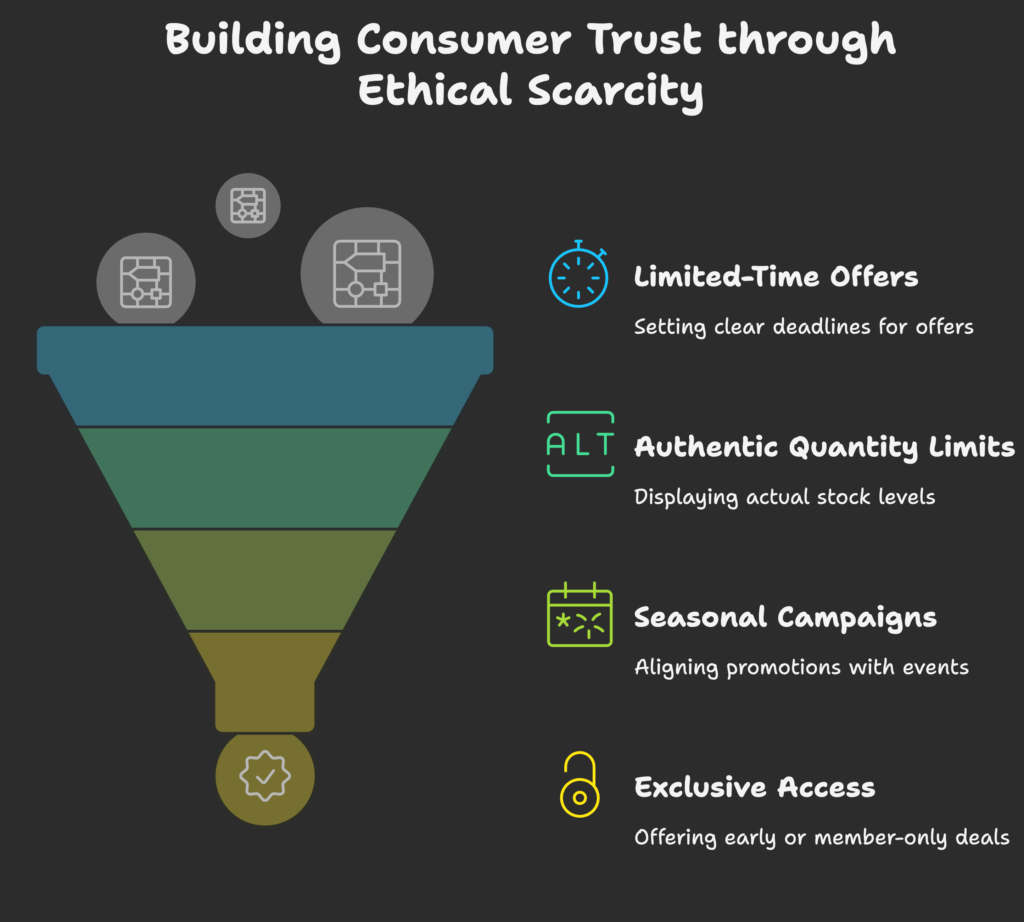
Genuine Limited-Time Offers
When you say an offer ends on a certain date, keep your word.
Use countdown timers that stop when the time is up, and communicate each deadline openly.
After the deadline, don’t quietly continue the same deal—it undermines trust.
Consumers appreciate honesty and will respect the real boundaries you set.
Next, let’s look at quantity limits and how to do them right.
Authentic Quantity Limitations
If you have a limited stock of an item, show the actual number available, or at least be clear that supplies are truly limited.
If it sells out, mark it as “sold out.” If you plan to restock, let people join a waitlist instead of pretending it’s gone forever.
When your claims match what customers see, they trust you more.
Now, what if your business is seasonal or event-based? Let’s explore that.
Seasonal and Event-Based Campaigns
Linking promotions to real events—like holiday sales or product launches—makes urgency natural.
Set a clear start and end date so customers know the window of opportunity.
Once the event is over, remove the offer.
This creates excitement that feels genuine and leaves customers looking forward to your next big occasion.
Some brands also give early access to loyal followers. Let’s see how that works.
Exclusive Access and Early Bird Incentives
Early bird deals reward people who act fast, but only if you truly limit the availability.
If you say “First 50 buyers get 20% off,” stick to that.
Creating a member-only sale can also add real exclusivity, as long as the membership itself is genuine.
Explain clearly who qualifies and why, so no one feels tricked.
These strategies are powerful, but how do we apply them across different marketing channels? Let’s see.
Implementation Across Marketing Channels
Here, we’ll look at how to adapt ethical scarcity for websites, email, social media, and paid ads.
Each platform has unique features, and you can optimize them without sacrificing honesty.

Website and E-commerce Platforms
On product pages, show real stock counts or genuine “low stock” indicators if they’re accurate.
During checkout, let shoppers know if time is truly limited for a discount.
Be sure the user experience remains friendly—avoid pop-ups that feel too pushy or confusing.
For mobile sites, keep messages short and easy to see, so buyers don’t feel overwhelmed.
Next, we’ll discuss how email campaigns can drive urgency responsibly.
Email Marketing Applications
Use clear subject lines, like “Sale ends Friday!” if that’s the real deadline.
Don’t send endless reminders every day with fake claims.
Inside the email, outline the main benefit and the actual timeline.
If a second reminder is necessary, keep it polite and factual—no need to scare or guilt people into buying.
Now, let’s see how to handle scarcity on social platforms.
Social Media Approaches
On social media, scarcity can go viral if done right. Show an authentic countdown or highlight a product’s fast-selling status.
Engage your community by explaining why the offer is limited, and encourage honest discussions rather than hard-sell tactics.
Sharing user-generated content, like posts from happy buyers, can add social proof without exaggeration.
Paid ads can also spread your message. Let’s talk about that next.
Paid Advertising Considerations
In ads, keep your statements consistent with your landing page.
If you say “24-hour deal” in the ad, make sure the timer is real on the landing page.
Also, avoid hitting the same audience with too many urgent ads, as this can feel spammy.
Check each platform’s rules to ensure you’re not violating any policies on misleading content.
Alright, we know how to implement scarcity across channels. Next, we’ll figure out how to measure our ethical success.
Testing and Measuring Ethical Effectiveness
In this section, we’ll see what metrics to watch, how to test your urgency levels, and what to do after a campaign ends.
You’ll learn to balance raw sales numbers with customer trust indicators.
Key Performance Indicators
Yes, conversion rates matter. But also pay attention to:
- Customer Satisfaction: Track ratings and feedback.
- Return Rate: Look at repeat purchases or subscription renewals.
- Brand Trust Surveys: See how comfortable customers feel with your tactics.
These metrics go beyond short-term revenue. They reveal how people truly feel about your brand.
Next, let’s learn how to test different urgency approaches without going overboard.
A/B Testing Frameworks for Ethical Optimization
Test small changes, like shorter or longer countdowns, or different phrases for a low-stock message.
Compare how each variant affects both conversion and customer feedback.
You might learn that a subtle approach works better than a highly aggressive one.
Segment your test groups by audience type—what works for first-time visitors may not work for repeat buyers.
Once the campaign is over, analyze your data for deeper insights. Let’s see how.
Post-Campaign Analysis
Review actual sales numbers versus the goals you set. Did you end the promotion at the promised time?
Did any customers complain about feeling misled?
Look at repeat purchase data to see if your approach built loyalty or just got one-time sales.
This helps you refine future campaigns and keep your brand reputation solid.
To make this more concrete, let’s look at real-life examples next.
Case Studies of Ethical Scarcity Implementation
In this section, we’ll explore companies and industries that successfully used honest urgency.
We’ll also see how small businesses with limited resources made a big impact with ethical scarcity.
E-commerce Success Stories
Some online stores share detailed stock levels on each product page, letting customers see the numbers drop in real time.
They end their promotions exactly at the announced time, reinforcing that “limited time” meant limited time indeed.
Sales go up without hurting trust, and customers leave positive reviews because they feel confident in their purchases.
What about service businesses, where the product isn’t physical? Let’s see next.
Service Industry Applications
Professional services, like consulting or online courses, can offer early-bird pricing with a genuine cutoff date.
Once the date passes, the price goes up.
This rewards those who commit sooner without faking scarcity.
Membership or loyalty programs also work if they truly give special perks and follow clear enrollment periods.
Small local shops can do this too, even on a tight budget. Keep reading!
Small Business and Limited Resource Examples
Local bakeries often announce “limited batches” of fresh pastries each morning.
This is honest because they can only bake so much in a day.
They might post a live update on social media when items are running low, creating real-time urgency without tricks.
A simple, genuine approach can be very effective, especially when tied to real constraints.
Now, let’s look ahead to future trends in ethical scarcity.
You might be surprised at how consumer awareness and technology are shaping new marketing norms.
Future Trends and Considerations
We’ll discuss how rising consumer awareness, new technologies, and changing cultural expectations are reshaping scarcity marketing.
Discover how to stay ahead of the curve while maintaining an ethical standard.
Evolving Consumer Awareness
Customers are getting better at spotting fake deals.
They also share their experiences widely on social media.
Brands that repeatedly use misleading tactics can quickly lose credibility.
This means honesty is becoming not just a moral choice but a practical one.
By providing clear details and backing up your claims with proof, you stand out in a crowded market.
Technology is also changing how we present scarcity. Let’s explore that next.
Technological Developments
AI can personalize urgency messages based on a user’s shopping history or behavior.
Blockchain might soon verify inventory in real time, preventing fake low-stock claims.
Meanwhile, advanced analytics let companies monitor the impact of their campaigns more accurately.
Embracing these tools responsibly can make ethical scarcity even more trustworthy and transparent.
Finally, let’s talk about the overall future of ethical marketing and why it’s more important than ever.
The Future of Ethical Marketing
As regulations grow tighter and consumers become more informed, ethical marketing will become a key competitive advantage.
Leaders in this space will shape best practices and raise industry standards.
By embedding ethics into your company culture, you ensure your brand stays relevant and respected, leading to more sustainable success.
We’ve journeyed through the many sides of scarcity and ethics. Let’s wrap it all up with final insights and practical steps.
The Sustainable Approach to Scarcity
In this last section, we’ll summarize key points, offer resources for continuous improvement, and highlight the long-term value of honest scarcity.
You’ll leave with a clear action plan for using ethical urgency in your own marketing.
Key Takeaways for Implementation
Here are the most important things to remember:
- Be Honest and Transparent: Show real deadlines and limits.
- Provide Genuine Value: Scarcity should highlight the product’s worth, not cover up a weak offer.
- Monitor Customer Sentiment: Keep an eye on feedback to ensure you’re building trust, not losing it.
- Stay Consistent: Let your marketing ethics match your actual business practices.
By following these principles, you set a strong foundation.
Next, we’ll see how to make ethical behavior part of your marketing culture.
Building a Culture of Ethical Marketing
Ethics in marketing starts at the top. Leaders who value honesty train their teams to think about customer well-being.
Regular discussions about ethical dilemmas help employees make better decisions in gray areas.
A structured framework for approvals and checks also keeps campaigns honest.
We’re almost done, but let’s add a final thought on how urgency and ethics can go hand in hand.
Final Thoughts on Balancing Urgency and Ethics
Ethical scarcity creates a win-win situation: your business can boost sales, and customers can make confident choices.
When trust grows, so does loyalty—and that’s the ultimate secret to sustainable success.
As marketers, we have the power to shape the way people feel about purchasing decisions.
Let’s use that power wisely and keep our industry moving in a positive direction.
By the way, if you own a Shopify store, don’t forget there’s a simple way to supercharge your sales: the Growth Suite app.
It’s designed to help you reach new levels of success while respecting your customers and keeping your marketing honest.
Give it a try and see how ethical scarcity can work for you!
References
- Rewriterapp.com. (2024, December 18). Ethical Concerns of Scarcity Tactics in Marketing. Link
- LinkedIn. (2023, December 1). How can you create urgency without resorting to manipulative tactics? Link
- OptinMonster. (2025, January 6). 34 Real-Life Examples of Scarcity Marketing to Boost Sales. Link
- Convin.ai. (2024, July 2). 10 Strategies on How to Create Urgency in Sales Without Pressure. Link
- The Chaos. (2025, January 4). Mastering FOMO Marketing: Strategies That Work. Link
- FasterCapital. (2000, January 1). What Is Ethical Persuasion And Why Is It Important For Business Success. Link
- Staxxer. (2025, January 24). The Illusion of Shortage: the Ethics of Artificial Scarcity. Link
- 9operators. (2024, March 25). Conditioning Customers for Urgency: Tactics and Ethics. Link
- Optimonk. (2024, November 4). Scarcity Marketing: 8 Powerful Ideas to Drive More Sales in 2025. Link
- Referralcandy. (2022, November 4). 19 Examples of the Scarcity Principle Used in Marketing. Link
- Cartboss.io. (2025, February 20). How to Create Urgency in Sales: 6 Proven Strategies That Drive Conversions. Link
- Lunas Consulting. (2022, June 1). How to Drive Urgency in Your Sales Process. Link
- The Canine Copywriter. (2025, January 6). Scarcity Marketing (plus 5 examples of when it’s sleazy). Link