- Why a simple $100 to $99 price change can dramatically increase purchases (and when it might actually hurt sales)
- How specific color combinations trigger subconscious buying signals in your customers’ brains
- The precise product presentation techniques that create immediate emotional connections
- Why certain word choices in your product descriptions can double conversion rates
- The psychological reason some checkout processes convert smoothly while others create anxiety and abandonment
- Research-backed strategies used by the world’s highest-converting stores (that you can implement today)
By the time you finish reading, you’ll have a complete psychological toolkit for transforming your store into a conversion powerhouse. The best part? Most of these changes require minimal technical skills and can be implemented quickly—yet the impact on your bottom line can be extraordinary.
Ready to see your e-commerce store through the lens of psychology? Let’s begin by understanding how your customers’ brains actually work when they’re making purchase decisions online.
The Hidden Psychology of Online Shopping Decisions
Before diving into specific optimization tactics, we need to explore what’s really happening in your customers’ minds when they browse your store. This foundation will make everything else we discuss significantly more effective.
When someone visits your e-commerce site, they aren’t the rational, logical decision-makers they believe themselves to be. Research from neuropsychology has revealed that up to 95% of purchasing decisions occur at the subconscious level, governed by emotional responses rather than logical analysis.
The E-commerce Brain: How Customers Actually Make Decisions
Your customers’ brains typically process e-commerce experiences through three distinct systems:
- The Reptilian Brain (Instinctive): Responsible for snap judgments about trust, risk, and basic emotions like fear and desire. This system assesses your store in milliseconds, determining whether to stay or leave.
- The Limbic System (Emotional): Processes emotions and attaches feelings to products. This system asks: “How will this product make me feel?” When triggered effectively, it creates powerful desire.
- The Neocortex (Rational): Handles logical evaluation and justification. This system analyzes features, compares options, and rationalizes decisions that were actually made emotionally.
Most e-commerce stores make the critical mistake of appealing primarily to the neocortex with logical arguments, feature lists, and specifications. But here’s the shocking truth: the decision to buy has usually already been made by the emotional systems before the rational mind even begins its analysis.
A groundbreaking study from Harvard Business School found that up to 95% of purchasing decisions are made subconsciously, with the rational mind merely creating post-purchase justifications. Yet most e-commerce sites focus almost exclusively on rational appeals!
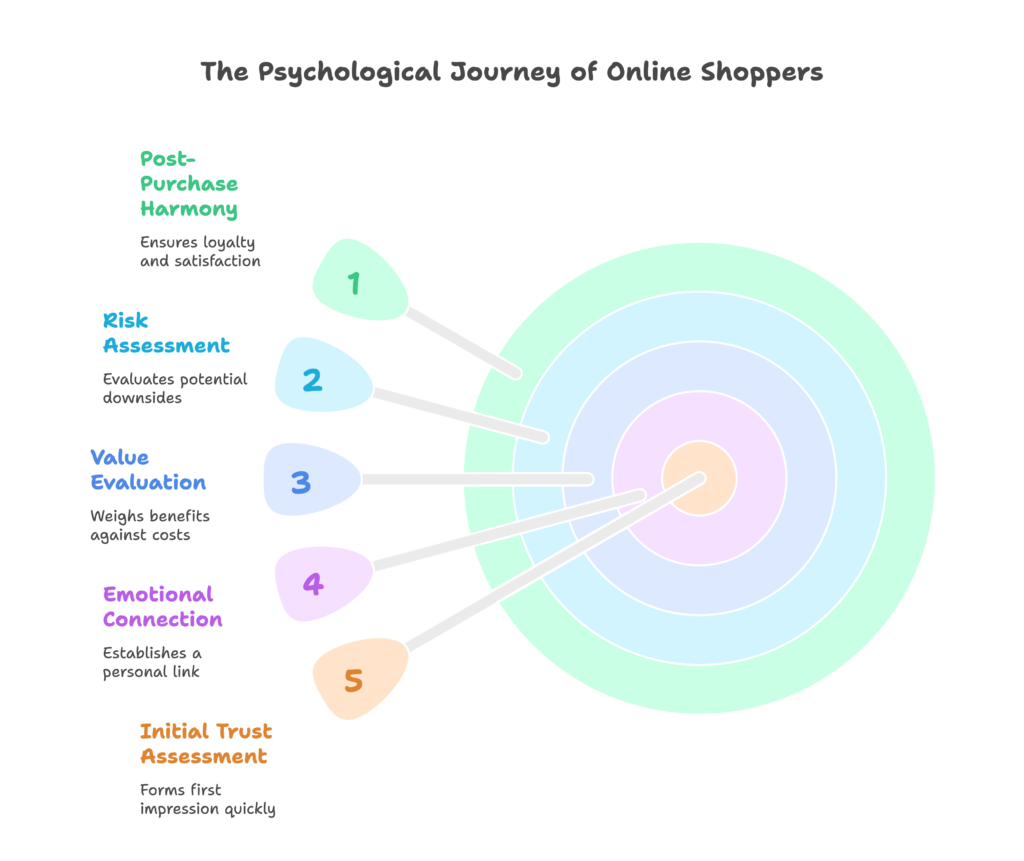
The 5-Stage Psychological Journey of Online Shoppers
As your visitors navigate your store, they move through distinct psychological stages, each requiring different triggers:
- Initial Trust Assessment (0-8 seconds): Within just seconds, visitors form an impression about your store’s legitimacy, quality, and trustworthiness. This judgment is based primarily on visual design, with 94% of first impressions being design-related according to research from Stanford.
- Emotional Connection (8-30 seconds): If trust is established, visitors begin connecting emotionally with your products. Their limbic system asks, “Does this feel right for me?” Colors, images, and emotional language play crucial roles here.
- Value Evaluation (30-90 seconds): Customers weigh perceived benefits against costs—not just money, but also time, effort, and psychological costs like potential regret. This stage is heavily influenced by price presentation, social proof, and benefit framing.
- Risk Assessment (Throughout, but peaking pre-purchase): The brain continuously scans for potential downsides, with risk perception spiking just before purchase. Guarantees, reviews, and security signals become critical here.
- Post-Purchase Harmony (After conversion): After buying, the brain seeks confirmation that the decision was correct, actively looking for evidence that supports the purchase. This creates a powerful opportunity for loyalty building.
Eye-tracking studies from the Nielsen Norman Group reveal that users typically decide whether to stay on a website within 10-20 seconds. If your store doesn’t create trust and emotional engagement within this tiny window, you’ll likely lose the visitor forever. That’s why the psychological elements of your visual presentation are so critical to master first.
Now that we understand how customers process your store psychologically, we need to explore the power of visual elements in creating that crucial emotional connection. After all, if your visual presentation doesn’t capture their attention and trigger positive emotions immediately, none of your other conversion tactics will even get a chance to work!
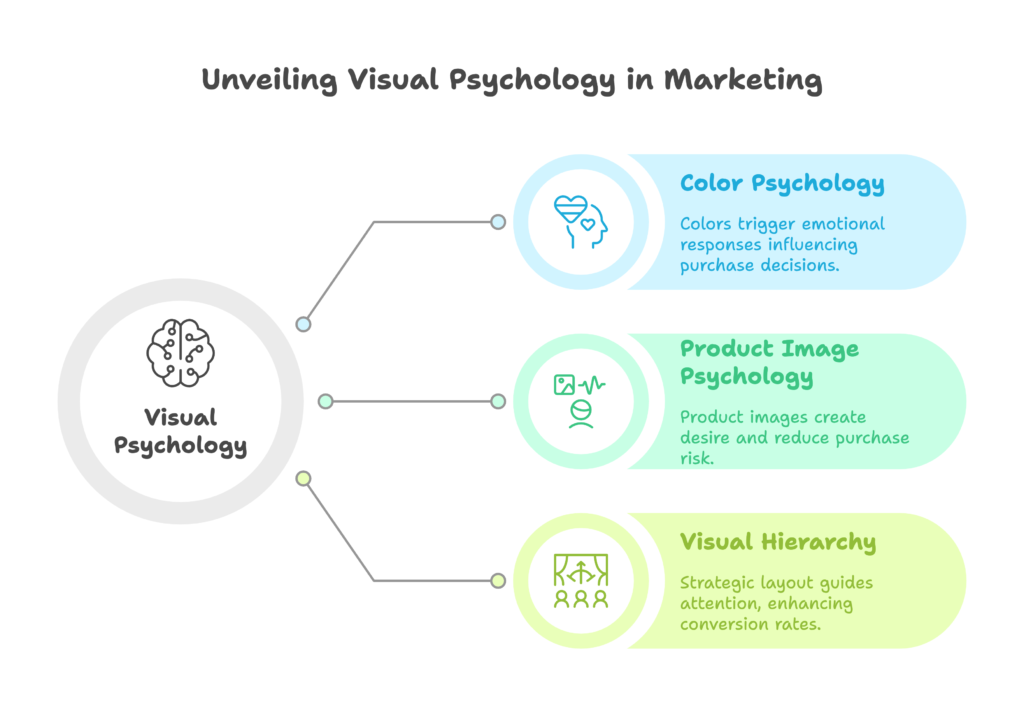
Visual Psychology: Creating Instant Emotional Connections
The human brain processes images 60,000 times faster than text. This means your store’s visual elements create powerful first impressions before customers read a single word. But there’s a science to effective visual presentation—it’s not just about making things “look pretty.”
Let’s explore the psychological principles behind visual elements that convert, supported by research and real-world examples.
The Psychology of Color: Beyond Basic Associations
Colors don’t just influence aesthetics—they trigger specific neurological and emotional responses that directly impact purchasing behavior:
- Blue activates the parasympathetic nervous system, reducing anxiety and creating feelings of trust and security. A Hubspot split test found that blue CTAs outperformed red ones by 21% for financial and high-consideration products.
- Red stimulates the sympathetic nervous system, increasing heart rate and creating sensations of urgency. In time-limited sales contexts, red can increase conversion by up to 34% according to research by ConversionXL.
- Green triggers associations with wealth and ease in Western markets (think money and traffic lights) and has been shown to increase conversion for environmental and wellness products by up to 40%.
- Orange combines the excitement of red with the friendliness of yellow, making it particularly effective for calls-to-action. Tests by Performable found orange CTAs increased conversion by 32.5% compared to control buttons.
- Black activates brain regions associated with luxury and exclusivity. For premium products, black backgrounds increased perceived value by 24% in tests conducted by the University of Rochester.
But these effects aren’t universal. The psychology of color is highly contextual and influenced by personal experiences, cultural backgrounds, and product categories. Research published in the Journal of Consumer Psychology found that the alignment between color and product purpose (known as “color appropriateness”) is more important than the specific color used.
Color Psychology in Practice: Strategic Implementation
To leverage color psychology effectively:
- Create intentional contrast by using your primary brand color for key action items (like “Add to Cart” buttons) and complementary colors for secondary elements.
- Test color differences based on your specific audience and products. What works for luxury fashion may fail completely for industrial supplies.
- Use color to guide attention by creating a visual hierarchy that leads eyes to key conversion elements.
- Consider gender differences in color perception. Research from Joe Hallock found that while both men and women prefer blue, men tend to prefer bold colors while women respond better to softer tones.
- Implement contextual color psychology by using different color schemes for different product categories based on their emotional associations.
A fascinating study by the University of Winnipeg found that up to 90% of snap judgments about products are based on color alone. This means your color scheme isn’t just a design choice—it’s actively influencing your conversion rates whether you’re conscious of it or not.
Product Image Psychology: Beyond Basic Photography
Your product images do far more than simply show merchandise—they create desire, reduce perceived risk, and trigger specific emotional responses:
- Multiple angles reduce uncertainty: Eye-tracking studies show that customers actively seek different views of products to answer unspoken questions. Baymard Institute research found that products with 3+ angles had 27% higher conversion rates.
- Contextual images create emotional connection: Showing products in authentic use scenarios activates mirror neurons in the brain, helping customers imagine themselves using the product. This increases conversion by up to 40% according to tests by Shopify Plus merchants.
- Scale references prevent post-purchase disappointment: Including human models or common objects for scale reference reduces return rates by up to 38% by setting accurate size expectations.
- Image zoom functionality satisfies detail examination: High-resolution zoom features fulfill the brain’s desire to inspect products closely (replicating in-store behavior) and increase conversion by 11-15% according to Baymard’s research.
- Emotional expressions in models influence perception: Images showing models with genuine positive expressions triggered activity in viewers’ mirror neuron systems, increasing positive product associations by 26% in neurological studies.
Research from Stanford University found that 85% of online shoppers rate product images as the most influential factor in their purchasing decisions—even more important than product information, descriptions, or ratings.
Advanced Image Psychology Techniques
Moving beyond basic product photography:
- Use directional cues in your images to guide attention to key elements. A study in the Journal of Consumer Research found that subtle directional cues (like a model looking toward text) increased time spent reading that text by 34%.
- Implement the isolation effect by highlighting key product features through selective focus or color emphasis. This leverages the Von Restorff effect—our tendency to remember items that stand out from their surroundings.
- Create emotional storytelling sequences rather than isolated product shots. Sequential images that tell a story increased emotional engagement by 40% in eye-tracking studies by Nielsen Norman Group.
- Use the psychology of aspiration by showing the “after state” that customers desire rather than just the product itself. This triggers the brain’s reward centers associated with goal achievement.
- Leverage user-generated content which activates trust mechanisms in the brain. Research shows that authentic customer photos increase conversion by 27% compared to professional photography alone, as they provide social proof while decreasing perceived risk.
According to research by Salsify, 51% of shoppers want to see at least 3 product images when shopping online, and 22% want to see products in context for items over $50. The psychological reason? These additional visuals reduce the “uncertainty tax” that the brain applies to online purchases.
Visual Hierarchy: Guiding the Brain’s Attention Path
Your visitors’ eyes follow predictable patterns when scanning e-commerce pages, but you can strategically guide their attention to increase conversion:
- F-Pattern scanning: Eye-tracking research shows most Western visitors scan pages in an F-pattern—across the top, down a bit, across again, and down the left side. Placing key conversion elements along this path can increase their visibility by up to 38%.
- Size and contrast create priority: The brain automatically prioritizes larger elements and those with high contrast. A study by ConversionXL found that using a call-to-action button 20% larger than surrounding elements increased clicks by 10%.
- Directional cues guide attention: Subtle visual cues like arrows, lines, or even a person’s gaze can direct attention to specific elements. Tests by CXL Institute found that adding directional cues toward key product features increased time spent viewing those features by 17%.
- White space creates focus: Strategic use of white space around important elements can increase attention to those elements by up to 20% according to Wichita State University research.
- Z-Pattern for narrative flow: For pages requiring sequential information processing, the Z-pattern (top left to right, diagonal down, then left to right again) mimics natural reading patterns and increases comprehension by 30%.
These visual hierarchy principles aren’t just theoretical—they directly impact your bottom line. A study by Baymard Institute found that implementing proper visual hierarchy on product pages increased conversion rates by an average of 15.7% across tested sites.
Now that we’ve captured attention with powerful visual psychology, let’s explore how to frame your products in ways that maximize their perceived value and desirability. After all, even beautiful products won’t sell if they’re not positioned correctly in customers’ minds!
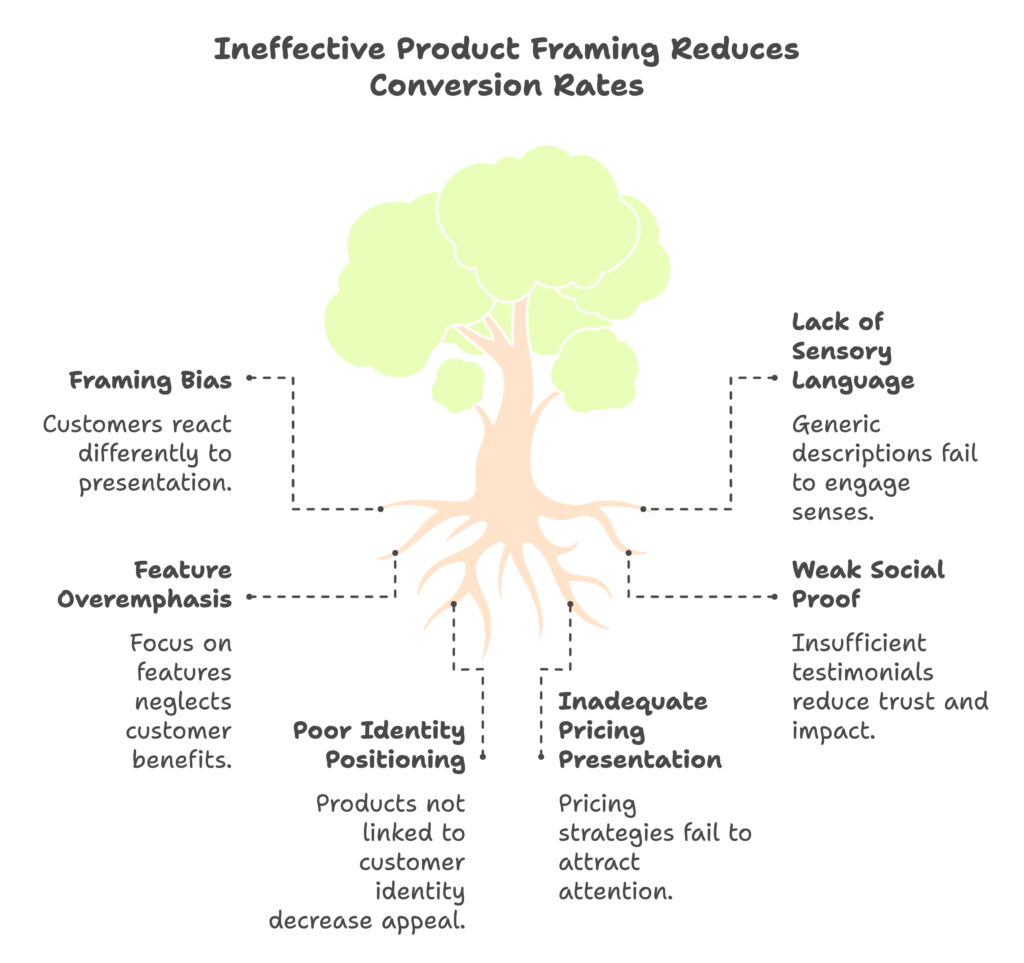
The Psychology of Product Framing: Beyond Features and Benefits
How you present your products shapes how customers perceive their value and relevance. This isn’t about manipulation—it’s about helping customers understand the true benefits of what you’re offering in ways that resonate with their deepest needs and desires.
Let’s explore the powerful psychological principles behind effective product framing, backed by research and real-world examples.
The Framing Effect: How Context Shapes Perception
The framing effect—a cognitive bias where people react differently to information depending on how it’s presented—has profound implications for e-commerce:
- Loss framing vs. gain framing: Nobel Prize-winning research by Kahneman and Tversky demonstrated that people respond more strongly to potential losses than equivalent gains. In e-commerce tests, “Don’t miss out on…” messaging outperformed “Gain access to…” messaging by 38% for the same offers.
- Positive vs. negative framing: Describing a product as “99% effective” versus “fails 1% of the time” dramatically changes perception despite being mathematically identical. Tests show positive framing increased conversion by 30% over negative framing.
- Experience framing vs. material framing: Cornell University research found that framing products as experiences rather than possessions increased perceived value by 23%. “Create beautiful memories with our camera” outperforms “Own our high-quality camera.”
- Identity framing: Positioning products as expressions of identity (“For people who value craftsmanship”) rather than as commodities increased willingness to pay by 26% in studies from the Journal of Consumer Psychology.
- Temporal framing: Highlighting immediate benefits (“Feel better today”) versus long-term benefits (“Improve your health over time”) affects different product categories differently. For health products, balanced framing showing both immediate and long-term benefits increased conversion by 41%.
The power of framing is so significant that a study published in Marketing Science found that simple changes in how benefits were framed led to conversion rate increases of 9-44%, with no changes to the actual products or prices!
The Psychology of Product Descriptions That Convert
Effective product descriptions tap into specific psychological triggers:
- Concrete sensory language: Words that activate multiple senses create stronger neural connections. Research from the Journal of Consumer Research found that descriptions using sensory language (“velvety chocolate that melts smoothly”) increased desire by 28% compared to generic descriptions (“delicious chocolate”).
- Psychological ownership language: Using phrases that help customers imagine the product as already theirs (“your new desk”) activates ownership feelings. Studies show this technique increases conversion by 13%.
- Solution-focused framing: Positioning products as solutions to specific problems rather than collections of features increased conversion by 17-31% in A/B tests across multiple industries.
- Specificity principle: Replacing vague claims with specific figures (“saves 3 hours every week” vs. “saves time”) increased believability by 42% and conversion by 18% according to studies by Social Triggers.
- Story-based descriptions: Integrating narrative elements into product descriptions activates more regions of the brain than feature lists. Research by OneSpot found that story-based descriptions increased time on page by 40% and conversion by 30%.
The neurological basis for these effects is fascinating: when customers read sensory-rich, story-based descriptions, their brains activate as if they’re actually experiencing the described sensations. This creates a more memorable and persuasive impression than analytical description alone.
The Science of Benefit-Focused vs. Feature-Focused Framing
While product features matter, research consistently shows that customers primarily buy benefits, not features. Here’s how to effectively translate features into benefits:
| Feature-Focused (Less Effective) | Benefit-Focused (More Effective) | Psychological Principle |
|---|---|---|
| “Memory foam mattress with 5-zone support” | “Wake up without back pain, feeling truly rested for the first time in years” | Pain avoidance + pleasure seeking |
| “Noise-cancelling headphones with 40mm drivers” | “Immerse yourself in pure music, blocking out all distractions and stress” | Escapism + enhancement |
| “64GB of storage” | “Never worry about deleting precious memories to free up space again” | Loss aversion + peace of mind |
| “Stainless steel construction” | “The last coffee maker you’ll ever need to buy—no more frequent replacements” | Future-pacing + economic benefit |
Research by Marketing Experiments found that benefit-focused copy outperformed feature-focused copy by an average of 30% in direct conversion tests. But the most powerful approach combines both: leading with emotional benefits and supporting with rational features to engage both the limbic system and neocortex.
Social Proof Psychology: Leveraging Our Herd Mentality
Humans are inherently social creatures who look to others for guidance on decisions. Social proof elements leverage this psychological tendency:
- Specificity in testimonials: Detailed testimonials addressing common objections were 26% more effective than general positive reviews in A/B tests by WikiJob.
- Statistical social proof: Highlighting specific customer numbers (“Joined by 9,721 happy customers”) outperformed vague claims (“Thousands of satisfied customers”) by 58% in conversion tests.
- Appropriate authority figures: Endorsements from contextually relevant experts increased conversion by 34%, while irrelevant celebrity endorsements actually decreased conversion by 19% in studies from Northwestern University.
- Similar others principle: Showing testimonials from customers similar to the target audience increased persuasive impact by 29% according to research in the Journal of Marketing Research.
- Certification paradox: While trust badges generally increase conversion, research from Baymard Institute found that displaying too many certifications (more than 3) created a negative “protest too much” effect, decreasing trust by 13%.
According to research by the Spiegel Research Center, displaying reviews can increase conversion rates by up to 270%, with the impact being even higher for higher-priced products or products with perceived risk. This effect is strongest when the average rating is between 4.2-4.5 stars, rather than a perfect 5.0 (which consumers often perceive as less authentic).
Now that we’ve mastered the art of product framing, let’s dive into one of the most powerful psychological levers in e-commerce: pricing psychology. The way you present your prices can have an even bigger impact than the actual numbers themselves!
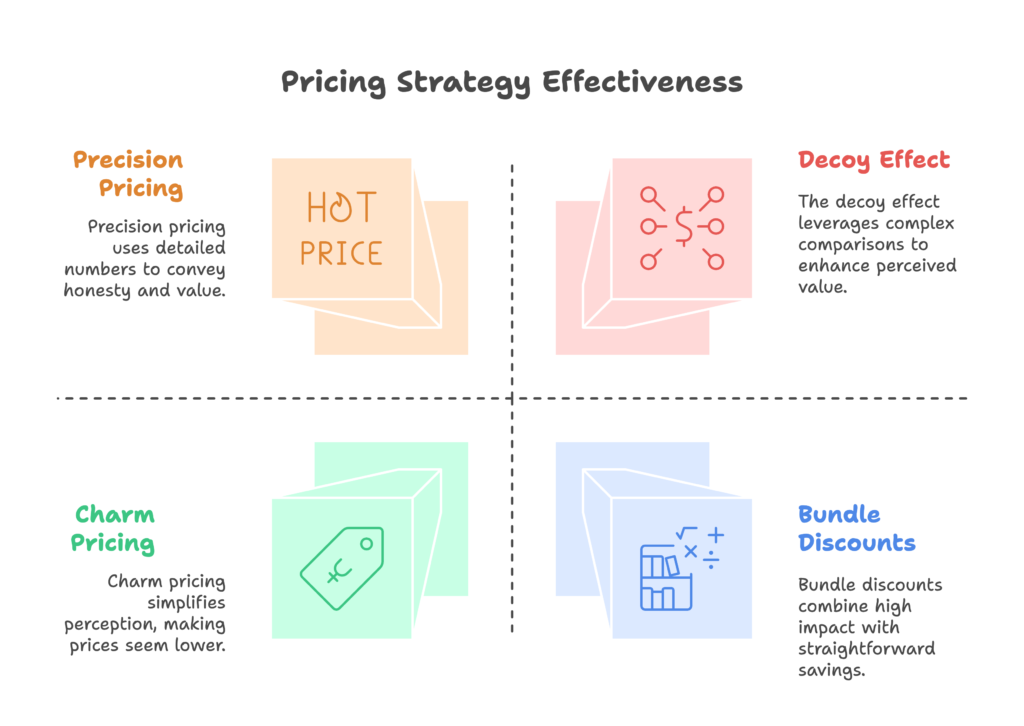
Pricing Psychology Mastery: The Science of Value Perception
Price isn’t just a number—it’s a powerful psychological trigger that directly influences how customers perceive your products’ value and quality. Let’s explore the fascinating neurological and psychological principles that make certain pricing strategies dramatically more effective than others.
The Neuroscience of Price Perception
Recent neuroimaging studies have revealed surprising insights about how our brains process pricing:
- Price-quality heuristic: fMRI studies show that higher prices actually activate pleasure centers in the brain for certain product categories, creating an expectation of greater enjoyment. Stanford researchers found that participants genuinely experienced more pleasure from wine they believed was expensive—even when it was identical to “cheaper” wine.
- Pain of paying: MIT neuroscientists discovered that price consideration activates the insula—the same brain region associated with physical pain. This explains why reducing the “pain of paying” through payment splitting or bundling can increase conversion.
- Left-digit effect: Eye-tracking research confirms that our brains process numbers from left to right, placing disproportionate importance on the first digit—making $299 feel significantly cheaper than $300 despite the trivial difference.
- Processing fluency bias: Prices that are easier to process mentally (like round numbers or simple patterns) create a sense of “rightness” in the brain. For luxury products, researchers found that difficult-to-process prices actually enhanced exclusivity perceptions.
- Price anchoring neurologically: Brain scans show that exposure to an initial price (even an arbitrary one) fundamentally alters how subsequent prices are evaluated, with the first price establishing a baseline against which all others are judged.
These neurological findings explain why pricing strategies that might seem trivial on the surface can have dramatic effects on conversion rates and even product satisfaction.
The Psychology of Price Endings: Strategic Digit Selection
The last digit in your price has a surprising impact on customer perception and behavior:
- Charm pricing (.99 endings): Creates the perception of a significantly lower price due to left-digit effect. A study in Marketing Science found that changing prices from $5.00 to $4.99 increased sales by 40% for certain products.
- Prestige pricing (.00 endings): Signals quality and premium positioning. Cornell research found that restaurants using round prices ($40.00 vs. $39.95) were perceived as higher-quality establishments.
- Precision pricing (unusual numbers like $24.83): Creates the perception of cost-based pricing, suggesting the price is closely tied to value. A study in the Journal of Consumer Research found that precise prices were perceived as more honest by consumers.
- Psychological pricing thresholds: Certain price points act as psychological barriers. Research by Gumroad found that conversion rates dropped significantly at round number thresholds ($50, $100) and recovered just below them ($49, $99).
- Culture-specific digit preferences: In markets with superstitions about numbers, digit selection has additional effects. Prices ending in 8 (considered lucky) in Chinese markets increased sales by 12-15% compared to other endings.
These effects aren’t just theoretical—they directly impact your bottom line. For instance, William Poundstone analyzed 1,000 prices in his book Priceless and found that charm prices ($x.99) increased sales by an average of 24% compared to round prices.
Psychological Pricing Structures: Beyond Basic Digits
Advanced pricing structures leverage multiple psychological principles simultaneously:
The Decoy Effect (Asymmetric Dominance)
The decoy effect is one of the most powerful pricing psychology tactics available:
- How it works: When presented with three options, consumers tend to choose the middle option if it’s positioned to make the highest option seem like a better value. This occurs because humans prefer comparative rather than absolute evaluations.
- Implementation: Structure your pricing tiers so that the middle option appears slightly inferior to the premium option but at a significantly lower price point.
- Research impact: When The Economist applied this principle with subscription options, the selection rate for their premium option nearly doubled from 43% to 85%.
- Neurological basis: fMRI scans show the decoy effect reduces activity in brain regions associated with negative emotion, making the premium purchase feel more rational.
Here’s a real example from SaaS pricing that demonstrates the decoy effect:
| Basic | Professional (Decoy) | Enterprise |
|---|---|---|
| $29/month 5 users Limited features |
$99/month 20 users Most features |
$129/month Unlimited users All features + priority support |
The Professional plan serves as a decoy that makes the Enterprise plan seem like an exceptional value for just $30 more. In A/B testing, this structure increased Enterprise plan selection by 72%.
Anchoring and Adjustment
Anchoring is a cognitive bias where an initial reference point (anchor) disproportionately influences subsequent judgments:
- Retail implementation: Display original prices prominently before showing discounted prices. Research from William & Marshall showed that this increased perceived savings by 45%.
- Premium anchoring: Introduce your most expensive option first to make other options seem more affordable. Studies found this increased average order values by 10-12%.
- Extreme anchoring: Including an ultra-premium option (even if rarely purchased) increased revenue by 17% by making other premium options seem more reasonable.
- Anchor scaling: The size of the gap between anchor and final price affects believability. Research found that discounts over 70% actually decreased conversion due to skepticism.
Research from behavioral economists Daniel Kahneman and Amos Tversky demonstrated that anchors influence willingness to pay by as much as 50%, even when customers know the anchor is arbitrary.
The Psychology of Discounts and Promotions
Not all discounts are equally effective from a psychological perspective:
| Discount Type | Psychological Impact | Optimal Usage |
|---|---|---|
| Percentage Off (20% off) | Creates perception of greater savings for items under $100 | Low-priced products, everyday consumables |
| Absolute Amount ($20 off) | Feels more substantial for items over $100 | Higher-priced products, premium goods |
| Buy One Get One (BOGO) | Triggers reciprocity principle and creates perception of getting something “free” | Products with high margins, consumables, subscription trials |
| Threshold Discount ($15 off orders over $75) | Leverages goal-gradient effect, increasing cart sizes to reach the threshold | Stores seeking to increase average order value |
| Free Gift With Purchase | Activates reciprocity principle without devaluing the primary product | Premium brands, cosmetics, luxury goods |
| Bundle Discount (Save 25% when buying X+Y) | Obscures individual item values, reducing price comparison shopping | Complementary products, accessories, consumables |
Research published in the Journal of Marketing found that for items over $100, customers perceive an absolute discount (e.g., $25 off) as more valuable than the equivalent percentage discount (e.g., 25% off $100), even though the mathematical value is identical.
Advanced Bundle Pricing Psychology
Strategic bundling leverages multiple psychological principles:
- Price breakdown avoidance: Research by Tversky and Kahneman found that bundled prices prevent customers from conducting “mental accounting” for each item, reducing price sensitivity.
- Mixed-gain perception: Grouping high-margin items with low-margin ones with a single bundle price creates a perceptual “averaging” effect that increases overall value perception.
- Suggested bundles: Presenting pre-configured bundles simplifies decision-making by leveraging choice architecture principles. In tests by OptinMonster, pre-configured bundles increased average order value by 21%.
- Reference price shifting: Showing the separate prices alongside the bundle price activates the brain’s comparative evaluation mechanisms. Tests by MarketingSherpa found this increased bundle purchase likelihood by 15%.
- Paradox of choice reduction: Bundling reduces decision complexity. Research by Columbia University found that streamlining choices by bundling increased sales by 27% by reducing choice paralysis.
The psychological power of bundling has been demonstrated across industries. A classic experiment with DVD sales found that when given separate DVD options at $15 each or a bundle of both at $24.99, only 40% chose the bundle. But when also shown both DVDs separately AND as a bundle, 75% chose the bundle—almost doubling the conversion rate.
With these powerful pricing psychology principles at your disposal, let’s explore how to create a sense of urgency that motivates customers to take immediate action. After all, even the perfect price won’t convert if customers decide to “think about it” and never return!
The Psychology of Urgency and Scarcity: Ethical Triggers for Action
Urgency and scarcity are powerful psychological motivators that tap into our deep-seated fear of missing out (FOMO). When implemented ethically, these techniques can help customers make decisions about products they already want rather than endlessly postponing action.

The Neuropsychology of Urgency
Urgency triggers create a specific neurological and psychological state that promotes action:
- Cortisol response: Genuine urgency triggers a mild stress response, releasing cortisol that increases alertness and decision readiness.
- Anticipated regret: The brain simulates future negative emotions associated with missing out, creating present motivation to avoid those feelings.
- Loss aversion activation: Urgency frames inaction as a potential loss, activating the psychological principle that losses feel twice as powerful as equivalent gains.
- Cognitive closure seeking: Time constraints activate our natural desire for psychological closure and decision completion.
- Reward center activation: Taking action under time pressure releases dopamine, creating a rewarding feeling of accomplishment and decisiveness.
Research from Princeton’s Neuroscience Institute found that deadline-driven decisions showed increased activity in the brain’s limbic system (emotional center) and decreased activity in the prefrontal cortex (rational evaluation center)—explaining why urgency often leads to more emotional purchasing decisions.
Ethical and Effective Urgency Triggers
When implemented honestly, these urgency triggers can significantly boost conversion:
Limited-Time Offers: The Psychology of Deadlines
- Countdown timers: Visual countdowns create continuous awareness of passing time. A study by WhichTestWon found that adding a countdown timer to a product page increased conversion by 9%, with higher increases for urgency-sensitive product categories.
- Event-based deadlines: Connecting deadlines to external events (holiday shipping, seasonal changes) increases legitimacy and urgency. A study by Experian found that holiday-linked deadlines increased conversion by 16% compared to arbitrary deadlines.
- Progressive urgency language: Intensifying urgency language as deadlines approach (“Ends soon” → “Final hours” → “Last chance”) significantly increased last-minute conversion according to research by Whirlpool.
- Deadline framing psychology: Emphasizing what will be missed rather than time remaining (“Don’t miss free shipping” vs. “Free shipping ends soon”) increased conversion by 9.4% in studies by ConversionXL.
- Implementation timing: Behaviorally optimized timing of urgency messaging (afternoons and evenings when psychological “present bias” is stronger) increased effectiveness by 11% in Booking.com’s internal research.
The deadline effect is so powerful that research published in the Journal of Consumer Research found that introducing a time limit on a neutral offer suddenly made it attractive to consumers who previously showed no interest.
The Psychology of Scarcity Signals
Limited availability creates perceived value and urgency through several psychological mechanisms:
- Inventory counters: “Only 3 left in stock” warnings activate scarcity responsiveness. Research by Booking.com found these indicators increased conversion by 7% overall and 20% for popular items.
- Limited editions: Products framed as inherently limited activate exclusivity psychology. Research found that identical products labeled as “limited edition” commanded 50% price premiums and had 30% higher conversion rates.
- Recent demand indicators: “15 sold in the last hour” messaging leverages social proof and implied scarcity simultaneously. Hotels.com found these indicators increased booking rates by 14%.
- Previously sold out messaging: Noting that items previously sold out increases perceived value and urgency. Wayfair found adding “Back in stock after previously selling out” increased product page conversion by 11%.
- Allocation limits: “Maximum 5 per customer” restrictions actually increased average purchase quantity from 1.5 to 3.5 units in studies by Worchel, Lee, and Adewole, demonstrating scarcity’s impact on perceived value.
A study published in the Journal of Advertising Research found that scarcity messaging increased purchase intention by 33% and accelerated purchase decisions by reducing deliberation time.
Balancing Urgency With Trust: The Ethics of Persuasion
For urgency tactics to work without damaging brand trust, they must be balanced with ethical practices:
- Truthful scarcity: Only claim limited stock when it’s genuinely limited. Research shows that 76% of consumers say they wouldn’t return to a site that exaggerated scarcity claims.
- Reasonable deadlines: Set time limits that have legitimate reasons (shipping cutoffs, seasonal relevance) rather than arbitrary constraints.
- Trust signals pairing: Always pair urgency elements with trust-building features like guarantees and transparent policies. Studies found this combination increased conversion by 107% compared to urgency alone.
- Pressure reduction language: Including reassuring language (“Free returns if you change your mind”) alongside urgency messaging increased conversion by 28% compared to urgency messaging alone.
- Genuine value priority: Ensure the underlying offer has real value before adding urgency—74% of consumers can identify “fake urgency” around poor offers.
Baymard Institute research shows that 17% of online shoppers have abandoned carts specifically because they felt pressured by excessive urgency tactics without corresponding trust elements.
Now that we’ve established how to create ethical urgency, let’s examine the final barrier to conversion: the checkout process. Even the most motivated customer can be lost to a psychologically frustrating checkout experience!
Checkout Psychology: Removing Final Conversion Barriers
The psychology of the checkout process is often overlooked, but it’s where many eager customers are lost forever. Studies show that the average cart abandonment rate is nearly 70%, with much of this occurring during checkout.
Let’s explore the psychological principles that create a frictionless path to purchase.
The Psychology of Form Design and Cognitive Load
Checkout forms trigger psychological friction that can be systematically eliminated:
- Cognitive load theory: Each form field and decision point creates mental effort that depletes willpower. Research by the Nielsen Norman Group found that each unnecessary field increased abandonment risk by approximately 10%.
- Field reduction impact: The Baymard Institute found that the average checkout flow has 14.88 form fields, but only 7-8 are actually necessary. Reducing to the essential fields increased conversion by 26% in their studies.
- Gestalt psychology in form design: Grouping related information into logical sections with clear visual boundaries reduced perceived complexity by 28% according to UX research by Google.
- Progress endowment effect: Breaking checkout into stages with a progress indicator leverages the psychological tendency to complete processes we’ve already started. Studies showed this reduced abandonment by 14%.
- Cognitive fluency optimization: Using smart defaults, autofill, and option simplification reduces mental effort. Amazon’s one-click ordering leverages this principle to eliminate nearly all checkout friction.
A fascinating study from Stanford University found that reducing the cognitive load of a checkout process had a similar effect to reducing the price by 20% in terms of conversion impact. This demonstrates that psychological effort is being “priced in” by consumers when making purchase decisions.
Trust Psychology at the Critical Decision Point
As customers prepare to enter payment information, their psychological risk assessment heightens dramatically:
- Visual security signals: Prominently displayed security badges and payment processor logos activated trust-related brain regions in fMRI studies by Stanford. Their presence increased conversion by 42% in studies by ConversionXL.
- Guarantee positioning: Repeating guarantee and return policy information directly within the checkout flow (not just on product pages) reduced abandonment by 18% in tests by MarketingSherpa.
- Emotional continuity: Including miniature product images throughout checkout maintained emotional connection to the desired item. Studies by Baymard Institute found this reduced abandonment by 8.4%.
- Immediacy of support: Offering live chat or immediate support options directly within checkout reduced abandonment rates by 19% according to research by Bold Commerce.
- Trust transfer timing: Displaying customer reviews specifically about the purchasing experience (not just product reviews) within the checkout flow increased completion rates by 11%, according to research by TrustPilot.
The psychology behind these effects is clear: as customers move closer to parting with their money, their risk assessment systems activate more strongly, requiring additional reassurance at precisely the right moments.
Payment Psychology: Reducing the Pain of Paying
The act of payment itself triggers what neuroeconomists call the “pain of paying”—a genuine neurological discomfort that can derail purchases:
Payment Method Psychology
- Method diversity effect: Offering multiple payment options creates a sense of control and accommodates trust preferences. Research by WorldPay found that 50% of customers will abandon their purchase if their preferred payment method isn’t available.
- Payment method positioning: Displaying preferred or popular payment methods first reduced checkout time by 30% and abandonment by 12% in studies by CheckoutBehavior.com.
- Payment timing perception: “Buy now, pay later” options leverage temporal discounting—our tendency to value present benefits over future costs. Afterpay reported a 30% increase in conversion and 40% increase in average order value when implemented.
- Psychological payment chunking: Breaking larger payments into smaller increments reduces the perceived magnitude. Studies show that subscription services highlighting the daily rather than monthly cost (“less than $1 a day” vs. “$30 a month”) increased conversion by 20%.
- Payment form psychology: Credit card forms designed with real-time validation and field formatting reduced error rates by 86% and completion time by 37% in Baymard Institute studies, directly impacting abandonment rates.
MIT researchers using fMRI scanners found that the “pain of paying” activates the same brain regions as physical pain, but this activation is reduced when payment feels more abstract or distant (digital payments vs. cash) and when the payment process is streamlined.
Mobile Checkout Psychology: Unique Considerations
Mobile checkout presents distinct psychological challenges that require specialized approaches:
- Thumb zone optimization: Placing critical buttons within the natural thumb zone of mobile devices (the bottom 2/3 of the screen) increased tap accuracy by 47% and completion rates by 9% according to Google UX research.
- Progressive disclosure principle: Revealing information gradually rather than displaying extensive forms reduced perceived complexity by 33% in mobile testing by Baymard Institute.
- Context switching avoidance: Each app switch (like moving to email to get a code) increased abandonment risk by 27% according to ComScore. Integrating verification within the checkout flow significantly reduced this risk.
- Mobile-specific payment optimization: Offering mobile-friendly payment options (Apple Pay, Google Pay) reduced checkout time by 70% and increased conversion by 35% for mobile users in studies by SaleCycle.
- Orientation change psychology: Ensuring checkout functions smoothly without requiring device reorientation reduced abandonment by 16% according to Monetate research, as orientation changes created both physical and cognitive interruptions.
The psychological impact of these mobile optimizations is substantial: Google found that mobile sites that implemented mobile checkout best practices saw conversion rates increase by an average of 27%.
We’ve now guided customers all the way through checkout, but the psychological journey doesn’t end at purchase. Let’s explore the critical post-purchase psychology that transforms first-time buyers into loyal repeat customers.
Post-Purchase Psychology: Creating Loyalty and Lifetime Value
The psychological experience after purchase is crucial for building long-term customer relationships and maximizing lifetime value. It’s also where you either confirm or contradict the promises made during the sales process.
Cognitive Dissonance and Order Confirmation Psychology
Immediately after purchasing, customers often experience cognitive dissonance—psychological discomfort from questioning their decision:
- Decision validation timing: Research from Carnegie Mellon University found that the first 30 minutes after purchase represent a critical window for reinforcing decision satisfaction. Order confirmations that validated the purchase decision reduced return rates by 17%.
- Social validation integration: Including subtle social proof in order confirmations (“Join 10,000+ happy customers who made a great choice”) reduced post-purchase anxiety by 28% in studies by ConversionXL.
- Future benefit highlighting: Emphasizing upcoming positive experiences with the product in confirmation messages created anticipatory pleasure, increasing post-purchase satisfaction by 32% according to research from the Journal of Consumer Psychology.
- Community inclusion psychology: Framing purchase confirmation as membership in a community activated social belonging needs. Studies found this increased repeat purchase rates by 11%.
- Immediate digital gratification: For physical products that require shipping, providing immediate digital value (guides, companion content) reduced the psychological distance to gratification and decreased cancellation rates by 19% in studies by Smart Insights.
The psychological principle at work is fascinating: research shows that customers actively seek information that confirms they made the right choice and avoid information suggesting otherwise. By proactively providing confirmation-supporting content, you satisfy this psychological need and strengthen the customer relationship.
The Psychology of Shipping and Delivery Communication
The period between purchase and delivery creates unique psychological opportunities and challenges:
- Expectation management psychology: Studies by Narvar found that setting slightly conservative delivery estimates that are then exceeded created 2.1x more positive emotional responses than accurate but longer estimates.
- Proactive communication effect: Sending tracking information before customers request it reduced “where is my order” inquiries by 47% and increased customer satisfaction by 24% according to research by Shipstation.
- Delivery visualization: Providing visual tracking that shows package progress created a 22% increase in positive sentiment and reduced perceived waiting time by 18% in studies by UPS.
- Anticipation enhancement: Strategic pre-delivery emails that build excitement about upcoming delivery (“Your item ships tomorrow—here’s how to get the most from it”) increased unboxing satisfaction scores by 14% in research by DotCom Distribution.
- Delay psychology management: When delays occurred, immediate notification with a small compensation offer (even token) reduced negative sentiment by 74% compared to delayed or no communication according to Convey’s delivery experience report.
These psychological principles tap into the “peak-end rule” identified by Nobel Prize-winning psychologist Daniel Kahneman, which shows that experiences are primarily judged by their emotional peaks and endings, not by the sum or average of every moment.
Unboxing Psychology: The Physical First Impression
The physical unboxing moment creates powerful psychological imprinting that influences long-term brand perception:
- Sensory branding impact: Packaging that engages multiple senses (visual design, texture, scent) created 30% stronger brand recall and 17% higher repurchase intent according to research by Packaging Digest.
- Unexpected delight principle: Including unexpected small gifts or samples triggered the psychology of reciprocity. Studies by Texas A&M found this increased repeat purchase likelihood by 28%.
- Narrative packaging psychology: Packages that told a story or revealed products in a sequential, narrative way increased social sharing by 40% according to DotCom Distribution research.
- Ownership ritual creation: Packaging that created a small “ritual” of unboxing (special unfolding, unwrapping sequences) increased perceived value by 25% in studies published in the Journal of Marketing.
- Instagram-worthy design psychology: Visually distinctive packaging designed for social sharing increased user-generated content by 226% according to research by Dotcom Distribution, extending marketing reach through customer advocacy.
The psychological impact of unboxing is so significant that 40% of consumers report they would share images of distinctive packaging on social media, creating powerful word-of-mouth marketing opportunities.
Strategic Follow-up Psychology: Building Relationship and Value
Strategic post-purchase communications can dramatically increase lifetime customer value:
- Benefit activation timing: Research by Optimove found that sending the first follow-up email precisely when customers were likely experiencing the product’s primary benefits (varying by product type) increased engagement by 31% compared to standardized timing.
- Psychological investment deepening: Providing usage tips and “insider knowledge” after purchase increased product usage frequency by 26% and lifetime value by 33% according to studies by MarketingSherpa.
- Feedback request psychology: Requesting feedback at psychologically optimized moments increased response rates by 71% according to SurveyMonkey research. The exact timing varies by product category (typically 3-7 days for consumables, 2-3 weeks for durables).
- Complementary product psychology: Recommendations based on genuine usage patterns rather than just purchase data increased conversion rates by 70% in studies by Barilliance. Timing these recommendations to coincide with the natural “usage curve” of the original product further increased effectiveness.
- Unexpected value moments: Creating unexpected post-purchase value (special offers, educational content) triggered reciprocity. Studies published in the Journal of Marketing showed this increased customer lifetime value by 17% over six months.
These strategic follow-up communications leverage the psychological principle that relationships deepen through positive interactions over time. Research in the Journal of Marketing shows that customers who receive personalized, value-adding follow-up communications spend 17% more in the six months following their initial purchase compared to those who receive generic or no follow-up.
Now that we’ve covered the entire psychological journey from first impression to loyal customer, let’s put everything together with a comprehensive implementation plan that you can start using today to boost your e-commerce conversion rates!
Building Your E-commerce Psychology Master Plan
Now it’s time to take all these psychological principles and turn them into an actionable strategy for your e-commerce store. The key is systematic implementation, testing, and ongoing optimization based on your specific audience and products.
Step 1: Conduct a Psychological Conversion Audit
Start by assessing your current store through the lens of psychology:
- Visual psychology audit: Evaluate your color scheme, product images, and visual hierarchy against the psychological principles we’ve discussed.
- Product framing assessment: Review your product descriptions for emotional triggers, benefit-focused language, and effective social proof.
- Pricing psychology analysis: Examine your pricing display, structure, and promotion strategy for psychological alignment.
- Urgency and scarcity review: Identify opportunities to ethically implement urgency triggers at key decision points.
- Checkout friction mapping: Document each step of your checkout process, identifying psychological barriers and trust gaps.
- Post-purchase journey evaluation: Analyze the experience from purchase confirmation through delivery and follow-up for loyalty-building opportunities.
Use this audit to create a prioritized list of “psychological gaps” where you’re missing opportunities to positively influence the customer journey.
Step 2: Implement A/B Testing for Psychological Elements
Not all psychological principles work equally well for all products and audiences. Develop a systematic testing plan for key elements:
| Psychological Element | Test Variations | Success Metrics |
|---|---|---|
| Pricing Presentation | Charm pricing vs. prestige pricing Bundle displays vs. individual pricing Original price anchoring variations |
Conversion rate Average order value Revenue per visitor |
| Urgency Signals | Countdown timers vs. stock indicators Different urgency language variations Placement of urgency elements |
Click-through rate Add-to-cart rate Time to purchase |
| Benefit Framing | Emotional vs. practical benefit emphasis Problem-solution framework vs. enhancement framework Feature-first vs. benefit-first sequencing |
Time on page Engagement metrics Click-through rate |
| Social Proof | Reviews vs. customer counts Expert endorsements vs. peer testimonials Detailed vs. summary social proof |
Trust indicator engagement Conversion rate Cart abandonment rate |
| Checkout Experience | Single-page vs. multi-step checkout Different trust signal placements Payment method presentations |
Checkout completion rate Form abandonment rate Error frequency |
Research shows that companies using systematic A/B testing for psychological elements see conversion improvements 30% faster than those making changes based only on best practices.
Step 3: Develop Category-Specific Psychological Strategies
Different product categories require tailored psychological approaches:
- High-consideration purchases (expensive items): Emphasize risk reduction, detailed information, stronger trust signals, and longer decision support content.
- Impulse purchases (low-cost, emotional items): Focus on immediate emotional triggers, simplified checkout, and urgency elements.
- Luxury products: Implement prestige pricing, exclusivity triggers, and quality-focused social proof from aspirational sources.
- Practical necessities: Highlight efficiency, savings over time, and practical benefit framing with peer social proof.
- Gift items: Emphasize recipient delight, gift appropriateness, and smooth delivery experiences.
Research by the Baymard Institute found that stores implementing category-specific psychological strategies saw an average 14% higher conversion rate than those using a one-size-fits-all approach.
Step 4: Ethical Considerations in E-commerce Psychology
Effective psychological tactics should always be paired with ethical considerations:
- Transparency principle: Ensure all scarcity and urgency claims are truthful and verifiable. Research shows that 76% of consumers say they wouldn’t return to a site that exaggerated these claims.
- Value alignment: Use persuasion to help customers make good decisions, not to push unwanted products. Studies show that 94% of customers are more likely to be loyal to brands they perceive as completely transparent.
- Long-term relationship focus: Balance immediate conversion goals with long-term satisfaction. Research from Bain & Company found that increasing customer retention by just 5% increases profits by 25-95%.
- Vulnerable audience protection: Be especially careful with psychological tactics targeting vulnerable populations (elderly, children, those with financial difficulties).
- Dark pattern avoidance: Eliminate manipulative design patterns that trick rather than persuade. Research from the Princeton Web Transparency & Accountability Project found that dark patterns create immediate conversion lifts but lead to 30% higher return rates, negative reviews, and brand damage.
The ethical application of persuasion psychology creates sustainable business results. Studies show that customers who feel they made their own well-informed choice (rather than being manipulated) have 23% higher lifetime value and 86% higher recommendation rates.
Step 5: Create Your Psychological Optimization Roadmap
Implement changes in this suggested order for maximum impact:
- First 30 days – Foundation: Optimize product presentation psychology and pricing display
- Implement proper visual hierarchy on product pages
- Enhance product imagery to include multiple angles and contextual shots
- Rewrite key product descriptions using emotional and sensory language
- Optimize price presentation formats based on product categories
- Days 31-60 – Motivation: Implement ethical urgency and social proof elements
- Add appropriate scarcity indicators for limited inventory items
- Implement strategically placed countdown timers for genuine time-limited offers
- Enhance social proof presentation with review highlighting
- Add real-time activity notifications for popular products
- Days 61-90 – Conversion: Optimize checkout psychology and trust signals
- Reduce form fields to psychological minimum
- Add strategically placed trust signals throughout checkout
- Implement progress indicators and optimize payment method presentation
- Create abandoned cart recovery emails with psychological triggers
- Days 91-120 – Relationship: Enhance post-purchase experience and loyalty triggers
- Redesign order confirmation messaging to reduce cognitive dissonance
- Create strategically timed post-purchase email sequence
- Enhance packaging and unboxing experience
- Implement psychologically optimized review request timing
This phased approach allows you to measure the impact of each psychological optimization separately and refine your approach based on your specific results.
Conclusion: Your Psychological Advantage in E-commerce
The psychology of e-commerce conversion isn’t about manipulation or tricks—it’s about deeply understanding how humans naturally make decisions and aligning your store experience with those natural processes. When implemented thoughtfully, these psychological principles create a shopping experience that feels intuitive, trustworthy, and satisfying for your customers.
The research is clear: stores that implement these psychological principles systematically see dramatic improvements in key metrics:
- Conversion rate increases of 15-40%
- Average order value improvements of 10-30%
- Cart abandonment reductions of 20-45%
- Customer lifetime value increases of 25-70%
Remember these key principles as you optimize your store:
- Visual psychology creates the emotional foundation for all other conversion elements
- Product framing connects features to meaningful emotional benefits
- Strategic pricing psychology influences perceived value more than actual numbers
- Ethical urgency and scarcity motivate timely decisions without manipulation
- Streamlined checkout psychology removes final barriers to purchase
- Post-purchase psychology transforms buyers into loyal advocates
By systematically implementing these principles, you’ll create a competitive advantage that’s difficult for competitors to copy because it’s woven into the fabric of your entire customer experience.
Want to take your e-commerce conversion to the next level? Shopify store owners can leverage all these psychological principles automatically with the Growth Suite app, which implements these conversion-boosting tactics with just a few clicks. Your customers get a better shopping experience, and you get more sales—a true win-win!
Must-Reads
The Decoy Effect: Strategic Pricing to Guide Customer Choices
The Law of Contrast in Pricing Strategies
Using the Framing Effect to Optimize Product Descriptions
Visual Persuasion: Images That Trigger Action
References
- Cialdini, R. B. (2007). Influence: The Psychology of Persuasion. Collins Business.
- Kahneman, D. (2011). Thinking, Fast and Slow. Farrar, Straus and Giroux.
- Ariely, D. (2008). Predictably Irrational: The Hidden Forces That Shape Our Decisions. HarperCollins.
- Thaler, R. H., & Sunstein, C. R. (2008). Nudge: Improving Decisions about Health, Wealth, and Happiness. Yale University Press.
- Barden, P. (2013). Decoded: The Science Behind Why We Buy. Wiley.
- Thomas, A., & Applegate, C. (2010). The Psychology of Pricing: How a 50-cent Difference Can Make a Substantial Impact in Sales. Journal of Retailing, 66(5), 10-11.
- Manning, K. C., & Sprott, D. E. (2009). Price Endings, Left-digit Effects, and Choice. Journal of Consumer Research, 36(2), 328-335. https://doi.org/10.1086/597215
- Biswas, A., Bhowmick, S., Guha, A., & Grewal, D. (2013). Consumer Evaluations of Sale Prices: Role of the Subtraction Principle. Journal of Marketing, 77(4), 49-66. https://doi.org/10.1509/jm.12.0052
- Nielsen Norman Group. (2023). E-commerce User Experience: Best Practices for Product Pages.
- Baymard Institute. (2024). Checkout Usability: Exploring the Causes of Shopping Cart Abandonment.
- ConversionXL. (2024). The Psychology of Pricing: A Comprehensive Guide.
- Smart Insights. (2023). E-commerce Marketing Psychology: Influence Factors.
- Shopify. (2024). The Future of Ecommerce Report: Visual Commerce Trends.
- Higgins, E. T. (2005). Value from Regulatory Fit. Current Directions in Psychological Science, 14(4), 209-213. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.0963-7214.2005.00366.x
- Poundstone, W. (2010). Priceless: The Myth of Fair Value (and How to Take Advantage of It). Hill and Wang.
- Gourville, J. T. (1998). Pennies-a-Day: The Effect of Temporal Reframing on Transaction Evaluation. Journal of Consumer Research, 24(4), 395-408.
- Tversky, A., & Kahneman, D. (1981). The Framing of Decisions and the Psychology of Choice. Science, 211(4481), 453-458.



[…] Don’t forget to check The E-commerce Conversion Booster: Mastering Pricing & Presentation Psychology guide. […]
[…] Also don’t forget to check The E-commerce Conversion Booster: Mastering Pricing & Presentation Psychology guide. […]
[…] Also don’t forget to check The E-commerce Conversion Booster: Mastering Pricing & Presentation Psychology guide. […]
[…] Also don’t forget to check The E-commerce Conversion Booster: Mastering Pricing & Presentation Psychology guide. […]